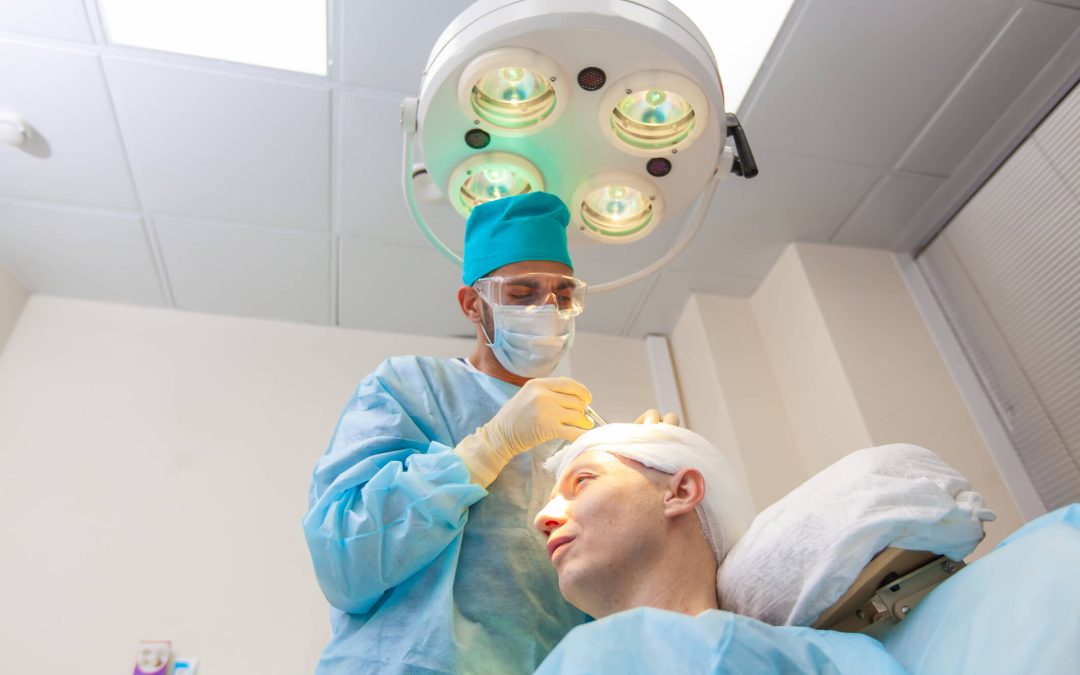
Hair restoration has become a transformative procedure for individuals seeking to regain their confidence and appearance. Among the most advanced options available is Neograft Hair Restoration, which is particularly popular in Orange County, where clinics emphasize cutting-edge technology and precision. While the results of these procedures are often life-changing, it’s essential to be aware of potential complications, including irritation or infections that may arise after hair transplant surgery.
Each graft transplant is vital to the overall outcome, and proper care is essential to avoid issues. Consulting a doctor for a thorough consultation before and after the procedure is crucial for identifying risks and understanding the steps needed to ensure optimal healing and results.
This guide will cover the key aspects of hair transplant infections, including their signs, causes, risks, and treatments. We’ll also discuss how proper aftercare and professional expertise can minimize risks and ensure the best results from your hair restoration procedure.
Understanding Hair Transplant Infections
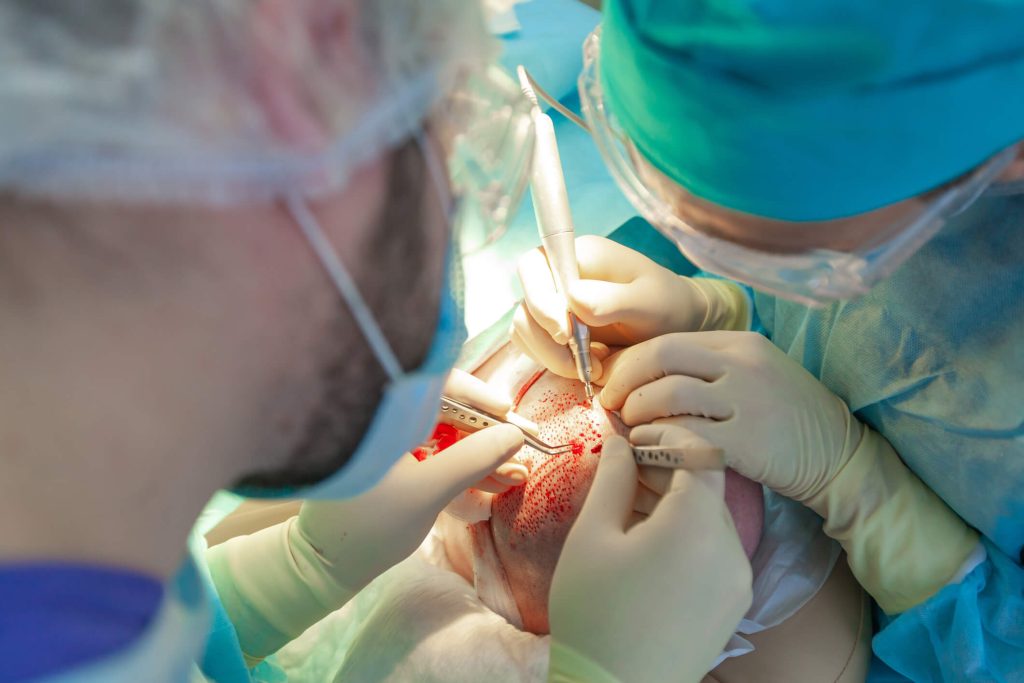
A hair transplant procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor site (often the back or sides of the scalp) to areas experiencing hair loss. Hair transplantation is a standard solution for addressing baldness or thinning hair. While techniques like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)—also known as the strip method—have high success rates, complications, such as infections or folliculitis, are always a possibility of complications, such as infections or folliculitis, especially if proper aftercare is not followed.
Each graft plays a critical role in the overall success of the hair restoration surgery, and taking precautions is essential. Factors like improper shampoo use, irritation at the donor site, or unexpected side effects can contribute to post-operative issues. Understanding how to minimize these risks is essential to ensure the best outcome for your specific case.
What Is a Hair Transplant Infection?
A hair transplant infection occurs when bacteria or other pathogens invade the surgical site, causing inflammation and discomfort. This can happen in the recipient area, the donor area, or both. Such infections can arise from various sources, including improper post-operative care or contamination during the procedure. Although rare, infections can compromise the healing process, affect the grafts, and require medical intervention to prevent long-term scars.
Infections may occur regardless of the types of hair transplant procedures performed, whether FUE, FUT, or other methods. They can also impact the effectiveness of hair transplants and lower the chances of achieving the desired results. Prompt treatment, often involving appropriate medications, is essential to address infections and protect the overall outcome.
Signs of Hair Transplant Infections
Recognizing the early signs of an infection is crucial for prompt treatment. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
- Redness and Swelling: Some redness is normal after a transplant, but prolonged or worsening redness, combined with swelling, may indicate infection.
- Pus or Discharge: The presence of pus or fluid drainage from the surgical site is a clear warning sign of infection.
- Pain and Tenderness: Persistent or increasing discomfort that doesn’t improve with time warrants immediate attention.
- Fever or Chills: A fever often indicates the body’s response to an infection.
- Crusting or Scabbing: While mild crusting is typical, excessive scabs that are inflamed or emit an odor may signify a problem.
- Bumps or Abscess Formation: Lumps filled with pus (abscesses) around the transplanted or donor areas are signs of localized infection.
Causes of Hair Transplant Infections
Understanding the causes of hair transplant infections can help patients and surgeons take preventative measures. Key causes include:
1.Lack of Hygiene Standards
Failure to maintain hygiene practices during or after the procedure is a leading cause of infections. Contaminated tools, improper sterilization, or unclean surgical environments can introduce harmful bacteria into the incisions.
2. Post-Procedure Neglect
Patients who neglect care instructions, such as cleaning the scalp or avoiding certain activities, may inadvertently expose the surgical site to infection. This can disrupt the healing process, particularly around sensitive areas like the hairline.
3. Bacteria on the Scalp
Even with precautions, bacteria on the skin can invade the tissue of the surgical incisions, especially if scabs or crusts are picked prematurely. This is why choosing the right type of aftercare is critical.
4. Underlying Health Conditions
Conditions like diabetes or compromised immune systems increase the risk of infection by slowing wound healing. For some people, these underlying issues may increase bleeding or delay recovery.
5. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or exposure to unsanitary environments post-surgery can also heighten infection risks. Addressing these factors can significantly improve the outcome of hair transplant procedures.
6. Lack of Research and Preparation
Patients who do not thoroughly research the procedure or read reliable articles and studies about hair transplant infections may need help understanding the necessary precautions. For patient safety, clinics should provide detailed information on how to prevent infections and discuss the potential risks during the consultation process.
7. Individual Associations and Conditions
Certain patients may be associated with autoimmune disorders or skin conditions that make them more susceptible to infections. A thorough medical history analysis can help identify these risk factors and allow for tailored prevention strategies.
Preventing infections requires a collaborative approach between the surgeon and the patient. Each one must play their part in maintaining a sterile environment, following instructions, and understanding their rights and responsibilities throughout the process.
Risks and Consequences of Hair Transplant Infections
While infections are generally manageable, untreated cases can lead to severe complications. Here are the potential risks:
1. Scarring
Infections can delay wound healing, resulting in excessive scarring in the donor or recipient area, which may significantly affect the overall aesthetic result. This can be especially concerning for individuals addressing pattern baldness or alopecia, as the goal is often a seamless, natural look.
2. Hair Follicle Loss
Inflamed or infected hair follicles may fail to grow new hair, reducing the success of the hair transplant procedure. This reaction can occur due to bacterial interference with the delicate tissue, especially in cases where infections are not promptly treated.
3. Systemic Infections
In rare instances, untreated infections can spread to other parts of the body, leading to severe conditions like septicemia. These systemic issues often begin with localized warmth, redness, and swelling at the surgical site.
4. Increased Discomfort
Infections often lead to prolonged pain, headaches, and tenderness, significantly complicating recovery. Healing activity may also slow, leaving patients with prolonged downtime and discomfort.
5. Emotional Impact
Beyond physical effects, complications can impact a patient’s mental health significantly if the outcome is compromised. For many men seeking to address pattern baldness, the procedure is not just about appearance but also about confidence and self-esteem. Any setback in their journey, mainly if associated with infections, can be emotionally challenging.
6. Age-Related Risks
Age can influence how the body responds to infections and the speed of healing. Older patients may experience a slower recovery and a heightened risk of infection-related complications due to reduced skin elasticity and immune function.
7. Warmth and Tenderness as Warning Signs
Persistent warmth around the surgical site can be a key indicator of an underlying infection. Recognizing these early signs and acting on them can help prevent escalation.
8. Informational Gaps
Lack of awareness about potential risks, often due to inadequate access to reliable articles or educational materials, can lead to improper post-surgical care. Patients should be well-informed about possible complications and how to manage them to ensure successful outcomes.
Infections are a rare but serious complication of hair transplantation. By understanding the risks and taking proactive measures, patients can minimize their chances of encountering such issues and enjoy the procedure’s transformative benefits.
Prevention of Hair Transplant Infections
Preventing infections begins with choosing the right clinic and following strict aftercare guidelines. Below are essential steps for minimizing infection risks:
1. Selecting a Skilled Surgeon
Choosing an experienced hair transplant surgeon ensures proper techniques and adherence to strict hygiene standards. Clinics specializing in procedures like Neograft Hair Restoration in Orange County prioritize patient safety and use advanced equipment.
2. Maintaining a Sterile Environment
Both the surgical facility and the patient’s post-operative care area should be kept clean and sterile to prevent bacterial growth.
3. Following Aftercare Instructions
Patients must strictly adhere to post-surgery instructions, including:
- Cleaning the scalp with prescribed shampoos.
- Avoiding contact with dirty hands.
- Wear clean clothing and avoid dusty environments.
- Refraining from smoking or drinking alcohol.
4. Monitoring Healing Progress
Regular follow-up visits with the clinic allow doctors to monitor the healing process and address any early signs of infection.
5. Leading a Healthy Lifestyle
A balanced diet, proper hydration, and sufficient rest support faster healing and reduce infection risks.
Treatment for Hair Transplant Infections
Despite precautions, infections can still occur. Early intervention is key to preventing severe complications. Here are common treatments:
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the first line of defense against bacterial infections. Oral or topical forms may be prescribed based on the severity.
2. Abscess Drainage
Surgical drainage may be necessary to remove pus and promote healing for more severe infections involving abscesses.
3. Proper Wound Care
Medicated compresses, cleaning solutions, and antiseptics can help control infections and support recovery.
4. Addressing Underlying Issues
If conditions like diabetes are contributing factors, managing these effectively is critical for recovery.
5. Follow-Up Procedures
In rare cases, additional procedures may be needed to address scarring, repair failed transplants, or replace damaged hair follicles.
Why Choose Neograft Hair Restoration in Orange County?
Neograft Hair Restoration is a minimally invasive option that offers natural-looking results with reduced downtime. Clinics in Orange County are renowned for their excellence in performing procedures like FUE and FUT, adhering to rigorous hygiene standards, and using advanced technology. These clinics follow sourcing guidelines to ensure the highest quality care and offer patients the best chance of a successful outcome.
Patients can expect:
- Comprehensive pre-surgery consultations to discuss risks, benefits, and expected outcomes, providing details about the entire process.
- Skilled surgeons who specialize in achieving seamless hairlines and maximizing follicular survival.
- Tailored aftercare plans to minimize infection risks and ensure optimal results, with careful attention to issues like itchiness, crust formation, and swelling.
Hair restoration is not just for men; these advanced procedures can also benefit women experiencing hair thinning or loss. Research from reputable research institutions and MDs has shown that hair transplants have a high success rate, mainly when performed by experienced professionals who understand the nuances of hair loss and management.
As with any medical procedure, patients need to educate themselves through trustworthy articles and sources, especially when it comes to post-surgical care. Whether it’s understanding the punches of the procedure or learning about potential condition risks, being well-prepared is crucial for the success of any surgery.
The course of recovery varies from person to person. Still, with proper management and adherence to aftercare instructions, anyone undergoing hair restoration surgery can expect significant improvement in the health of their hair and overall appearance.
The Role of Aftercare in Preventing Infections
Aftercare plays a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth recovery. Here are detailed aftercare tips to prevent infections:
Cleaning and Hygiene
- Use only the recommended shampoos and cleaning products.
- Avoid touching the surgical site with unwashed hands.
Avoiding Strenuous Activities
- Postpone heavy exercise or activities that cause sweating, as these can introduce bacteria.
Protecting the Scalp
- Avoid direct sun exposure and protect the scalp from dust and pollution.
Medication Adherence
- Follow the prescribed medication schedule, including antibiotics, to prevent bacterial growth.
Monitoring for Signs of Infection
- Be vigilant about symptoms like redness, swelling, or pus, and report them immediately to your hair transplant surgeon.
Final Thoughts
A successful hair restoration journey requires advanced surgical techniques, diligent aftercare, and proactive communication with your medical team. By understanding the risks of hair transplant infections and taking steps to prevent them, you can confidently pursue a transformative procedure like Neograft Hair Restoration in Orange County.
For personalized consultations, expert advice, or more information, contact our clinic by phone today. Let us help you achieve a confident, full head of hair while prioritizing your health and safety!
We are committed to providing the best care at every stage of your hair restoration journey, whether it’s a follicular unit transplant or another method. If you have questions about the procedure, potential damage risks, or the names of specific treatments, we have reliable evidence and information to guide you. Explore our blogs and articles addressing common concerns such as hair grafts, aftercare instructions, and how to avoid complications.
No matter the fact, we ensure all of your concerns are met, from your first appointment to the final stages of recovery. We recommend secure compresses or other appropriate aftercare products to support healing. Our medical team is dedicated to answering all your questions to ensure a smooth recovery and the best possible results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes hair transplant infections?
Several factors can cause hair transplant infections, including poor hygiene during the procedure, contamination from bacteria on the scalp, or inadequate aftercare. Health conditions such as diabetes can also increase the risk of infection.
How do I know if I have a hair transplant infection?
Symptoms of infection after a hair transplant can include redness, swelling, pus or discharge from the surgical site, fever, pain, tenderness, crusting, and abscesses. If you experience these symptoms, you must contact your doctor for evaluation and treatment.
Can hair transplant infections affect the results of the procedure?
Yes, infections can affect the outcome of your hair transplant. If not treated promptly, infections can lead to scarring, hair follicle loss, or delayed healing, which may negatively impact the procedure’s final results.
How can I prevent infections after my hair transplant?
To reduce the risk of infection, follow your surgeon’s aftercare instructions closely. Maintain proper hygiene, avoid touching the transplanted area with unclean hands, avoid heavy physical activity, and refrain from smoking or drinking alcohol post-surgery.
What treatments are available for hair transplant infections?
Treatment typically includes antibiotics, either oral or topical, to target bacterial infections. In more severe cases, abscess drainage may be necessary to remove pus and reduce inflammation.
How long does it take to recover from a hair transplant infection?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the infection. Mild infections can be resolved with antibiotics and proper care within a few weeks, while more severe infections may require additional treatments and a more extended recovery period.
Can I exercise after a hair transplant?
It is advisable to avoid strenuous physical activities, including exercise, for at least a few weeks after the procedure. This helps prevent sweating and potential bacterial exposure to the surgical site, which can increase the risk of infection.
What role does my surgeon play in preventing infections?
A skilled surgeon will ensure the surgical environment is sterile, use proper tools and techniques, and provide you with comprehensive aftercare instructions to reduce infection risks. Regular follow-up visits allow the surgeon to monitor your recovery and intervene if any issues arise.
Are there any lifestyle changes I should make to prevent infections?
To improve your chances of a successful hair transplant, maintain a healthy lifestyle. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, as these can interfere with the healing process and increase infection risks. Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting adequate rest can support faster recovery.
Is it normal to experience some discomfort or irritation after the procedure?
Yes, some discomfort, irritation, and minor swelling are expected during the initial stages of recovery. However, if these symptoms persist or worsen or notice signs of infection, you should consult your doctor for further evaluation and treatment.












Recent Comments