Spironolactone is a medication frequently prescribed to treat conditions like high blood pressure, heart failure, and hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). While it effectively manages these conditions, many are concerned about its potential side effects, particularly regarding hair health. A common question is whether spironolactone causes hair loss. Studies show that spironolactone, or Aldactone, blocks sex hormones and may contribute to hair shedding in some individuals, especially at higher doses. However, this is often temporary. Some people may experience side effects like headaches or fluid retention, and lifestyle changes may also occur. The FDA has approved spironolactone for specific uses, but it’s essential to consult your doctor to understand the risks and determine the correct dose for your needs. Your doctor can help you navigate the potential effects on your health.
Understanding Spironolactone and Its Effects on the Body
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic that helps the body eliminate excess sodium and water while preserving potassium. It also inhibits the effects of male hormones (androgens) like testosterone, which are known for their antiandrogen properties. This is particularly beneficial for conditions like PCOS, which can cause symptoms such as acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and hair thinning due to high levels of androgens. Spironolactone has been shown to improve sebum production and acne, offering an effective treatment option. However, it may also cause side effects like diarrhea, lightheadedness, and a decrease in sex drive. In rare cases, hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) can occur. Monitoring these signs and consulting a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential. Hair transplants or other treatment options may be necessary to address hair thinning or loss.
The Relationship Between Hair Loss and Spironolactone
Although spironolactone is frequently prescribed to address hair loss caused by androgenic alopecia, a hormonal imbalance-related condition characterized by hair thinning, certain individuals may experience hair loss as a side effect of the medication. Although this may be counterintuitive, there are a few potential explanations.
- Initial Shedding Phase: Shedding is prevalent during the initial phase of spironolactone therapy. Hair loss may be apparent as the body adjusts to the medication, which may temporarily induce the shedding phase in mature hair follicles. This is typically a temporary issue; many individuals experience hair regrowth after a few months as their hair cycle stabilizes.
- Hormonal Modifications: Spironolactone may alter the body’s hormonal equilibrium, influencing androgen levels. This change may initially result in hair thinning or loss for some individuals, mainly if the body is susceptible to hormonal fluctuations. Nevertheless, this phenomenon is transient for some individuals and can be resolved with time.
- Underlying Conditions: In certain instances, hair loss may not be directly caused by spironolactone but rather by the condition it is being treated for. For instance, individuals with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may experience hair thinning as a symptom of the condition. Spironolactone may prevent additional hair loss by inhibiting androgens. Nevertheless, hair loss may persist if the condition is not adequately addressed.
Comparison with Other Medications
A variety of medications are frequently prescribed to treat hair loss, which is mainly due to hormonal imbalances or conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Each possesses a distinctive mechanism of action, benefits, and potential adverse effects. In this section, we will compare spironolactone with other commonly used medications for hair loss, such as finasteride, minoxidil, and oral contraceptives.
Finasteride vs. Spironolactone
Finasteride (Propecia) is an additional medication frequently employed to address hair loss, mainly androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness) in both men and women. Like spironolactone, finasteride functions by inhibiting the effects of androgens; however, it accomplishes this through an alternative mechanism.
Mechanism of Action:
- Spironolactone is an antiandrogen that inhibits androgen receptors and decreases testosterone production and other masculine hormones.
- Finasteride inhibits the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Thus, finasteride mitigates hair loss by decreasing the levels of DHT, which is a critical factor in androgenic alopecia.
Efficiency:
- Spironolactone is generally more effective for women, particularly those with hormonal imbalances such as PCOS, as it addresses both hair loss and excessive hair growth (hirsutism).
- Finasteride is more frequently prescribed to men, but it can also be beneficial for women who have androgenic alopecia. Nevertheless, it is not generally recommended for women of reproductive age due to the possibility of congenital disabilities.
Consequences:
- Dizziness, irregular menstrual cycles, and elevated potassium levels are potential adverse effects of spironolactone. As the body adjusts, it may also result in transient hair loss.
- Erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and decreased semen volume are potential sexual adverse effects of finasteride. These adverse effects are more prevalent in men but may also manifest in women.
Minoxidil vs. Spironolactone
Minoxidil (brand name Rogaine) is a topical solution for hair loss in men and women. Unlike spironolactone, it is administered orally to the cranium.
Mechanism of Action:
- Spironolactone functions by inhibiting androgens, which can help mitigate hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances.
- Minoxidil stimulates hair follicles by enhancing blood circulation to the cranium and fostering hair growth. It does not address the hormonal causes of hair loss; however, it can assist in hair regrowth in individuals experiencing thinning.
Efficiency:
- Spironolactone is notably effective for women who have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other hormonal causes of hair loss. It can also assist in reducing profuse hair growth in undesirable regions.
- Minoxidil is frequently employed as a primary treatment for general hair depletion and is effective for both men and women with androgenic alopecia. It is especially beneficial for hair regrowth but may not be as effective in resolving underlying hormonal imbalances.
Consequences:
- Spironolactone may induce systemic adverse effects, such as fluctuations in potassium levels, vertigo, and menstrual irregularities.
- Minoxidil is generally well-tolerated but may induce scalp irritation, dehydration, and unwanted facial hair growth in certain instances.
Oral Contraceptives vs. Spironolactone
Women with hormonal hair loss, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), are occasionally prescribed oral contraceptives (birth control tablets). Synthetic hormones are present in these tablets, which regulate the menstrual cycle and decrease androgen production.
Mechanism of Action:
- Spironolactone inhibits androgen receptors and diminishes testosterone’s effects, resulting in diminished hair loss and less excessive hair growth.
- Oral contraceptives are composed of estrogen and progestin, which are capable of regulating hormonal fluctuations and reducing androgen levels, which may contribute to hair thinning.
Efficiency:
- Spironolactone is frequently prescribed in conjunction with oral contraceptives for women with PCOS to address both hair loss and hirsutism. It can be more effective when used in conjunction with birth control.
- In women with hormonal imbalances, oral contraceptives can be effective in reducing hair loss; however, they may not be as effective for those with significant androgenic alopecia. They are frequently employed as a preventive measure or with other interventions.
Consequences:
- Dizziness, irregular menstrual cycles, and elevated potassium levels are potential adverse effects of spironolactone.
- Nausea, weight gain, and mood swings are potential adverse effects of oral contraceptives. Additionally, they may elevate the likelihood of blood clotting in specific individuals.
Dutasteride vs. Spironolactone
Dutasteride (sold under the brand name Avodart) is comparable to finasteride in that it prevents the conversion of testosterone to DHT. However, it is more potent and inhibits both varieties of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme.
Mechanism of Action:
- Spironolactone inhibits the generation of testosterone by blocking androgen receptors.
- Dutasteride inhibits 5-alpha reductase, thereby decreasing DHT levels and aiding in treating hair loss caused by DHT sensitivity.
Efficiency:
- Spironolactone is notably beneficial for women who have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other hormonal imbalances.
- In the treatment of male-pattern baldness, dutasteride may be more effective than finasteride; however, it is not typically prescribed to women due to potential risks incurred during pregnancy.
Consequences:
- Dizziness, elevated potassium levels, and irregular menstrual cycles are potential side effects of spironolactone.
- Finasteride and dutasteride both have comparable adverse effects, such as sexual dysfunction; however, the latter may be more prevalent.
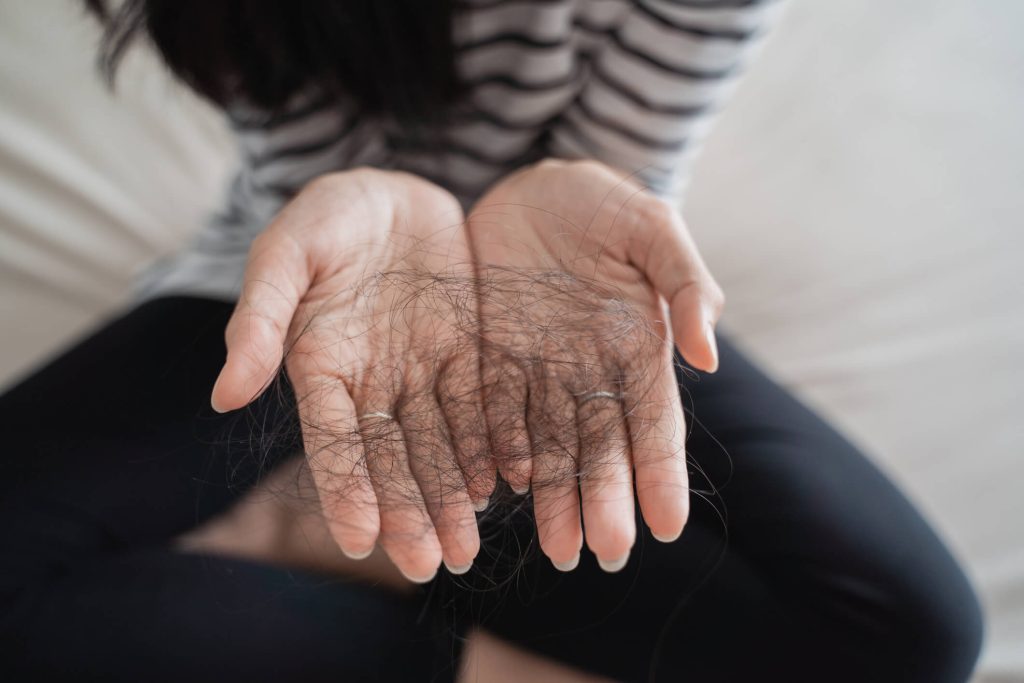

Client that is Taking Spironolactone having a Hair Loss Problem in Orange County, California
How Spironolactone Can Assist in the Prevention of Hair Loss
Intriguingly, spironolactone is frequently prescribed as a treatment for androgenic alopecia, a prevalent form of hair loss that affects both men and women. Spironolactone can help reduce hair depletion and promote hair regrowth by inhibiting the effects of androgens. This medication may serve as an advantageous component of an extensive hair restoration regimen for numerous individuals.
By reducing androgen levels, spironolactone can address the underlying cause of hair loss in women with PCOS. This can assist in reducing excessive hair growth on the face and body while fostering healthier scalp hair growth. Research has demonstrated that spironolactone can enhance hair density and decrease discharge in women experiencing hormonal hair loss.
What to Do if You Experience Hair Loss While Taking Spironolactone
It is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider if you are experiencing hair loss while taking spironolactone. They can assist in determining whether the hair loss is a consequence of the medication or is associated with an underlying condition. In most instances, the shedding will be transient and subside as your body adjusts to the medication. However, if the hair loss persists or worsens, your physician may suggest adjusting your dosage, trying different medication, or incorporating combination therapy options, such as minoxidil or other antiandrogen products. In some cases, a hair transplant may be considered. Your doctor will also guide you through sourcing guidelines and associations related to hair loss treatments, helping you find the best ways to manage your condition and improve hair regrowth. Understanding your rights and treatment options is essential to making informed decisions about your hair restoration journey.
Conclusion
Spironolactone is a prescription drug that can affect various conditions, including hair loss and shedding. It is known to balance skin retention and treat high blood pressure, but its use may lead to side effects such as breast tenderness, stress, and changes in urination. While some patients may experience temporary hair loss or initial shedding, studies, and reviews, suggest that it can effectively treat androgenic alopecia and hair thinning caused by hormonal imbalances. Dermatologists and doctors recommend monitoring the drug’s effectiveness for each patient. If you are concerned about hair loss or other side effects, consult your healthcare provider to review the evidence and determine the best action.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does spironolactone influence the texture of hair?
Although spironolactone predominantly affects hair growth by blocking androgenic hormones, some individuals may experience changes in their hair’s texture due to medication or as part of the regrowth process. These modifications are typically transient and should be resolved upon the hair cycle’s stabilization. Consult your healthcare provider for guidance if you observe substantial alterations.
Are there any alternatives to spironolactone for the treatment of hair loss?
Indeed, there are numerous alternatives to spironolactone for treating hair loss, contingent upon the underlying cause. Laser therapy, finasteride (for men), minoxidil, and other antiandrogen medications are viable alternatives. Your healthcare provider can assist in determining the most suitable treatment for your unique health requirements and condition.
How can I determine whether spironolactone is the cause of my hair loss?
Hair loss may be associated with spironolactone, mainly if it occurs concurrently with the commencement of treatment. Nevertheless, other factors, such as underlying health conditions or other medications, may also be involved. Consult with your healthcare provider to ascertain the cause and to deliberate on any required modifications to your treatment regimen.
If I experience hair loss, is it safe to discontinue my spironolactone treatment?
If you are experiencing hair loss while taking spironolactone, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider before discontinuing the medication. AA precipitous cessation of medication could impact your treatment for the underlying condition for which it was prescribed. Your physician can assist in determining the optimal course of action, which may entail modifying the dosage or transitioning to an alternative medication.
Can spironolactone be combined with other hair loss treatments?
Indeed, spironolactone is frequently used with other hair loss treatments, including minoxidil and finasteride (for men). Nevertheless, consulting with your healthcare provider is crucial to guarantee that any combination of remedies is safe and suitable for your unique circumstances.
Is spironolactone effective in the treatment of male pattern baldness?
Spironolactone is not frequently employed to address male pattern baldness due to its potential to induce feminization in men. It is more frequently prescribed to women with androgenic alopecia, particularly when the condition is associated with hormonal imbalances, such as those observed in PCOS. Other remedies, such as finasteride, are typically used to treat hair loss in men.
Is it possible for spironolactone to induce hair loss in women?
Indeed, spironolactone is frequently prescribed to address hair loss in women. However, some individuals may experience temporary shedding upon initiating the medication. This may occur as the body adjusts to the hormonal changes caused by spironolactone. Nevertheless, this shedding is transient for many women, and hair regrowth occurs after the body achieves equilibrium.
Is it possible for spironolactone to cause permanent hair thinning?
Spironolactone’s effects on hair loss are typically temporary, making permanent hair thinning unlikely. Nevertheless, hair thinning may persist if the underlying condition causing the hair loss is not entirely addressed or if there are other contributing factors. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can facilitate managing and monitoring ongoing issues.
Is it possible for spironolactone to exacerbate hair loss?
Although spironolactone is typically prescribed to address hair loss, some individuals may experience an initial increase in thinning during the initial weeks or months of treatment. This is typically a temporary occurrence and a component of the acclimation process as the body responds to the medication. Nevertheless, it is crucial to seek the advice of a healthcare provider if hair loss persists or worsens.
How long does it take to observe results from spironolactone for hair loss?
Significant results from spironolactone for hair regrowth may require several months (usually 3 to 6) to observe. As hair growth is gradual, maintaining a consistent approach to treatment and being patient is crucial. If no improvement is observed after this period, it is recommended that you seek additional advice from your healthcare provider.
Understanding How Spironolactone Can Affect Hair Loss
Observing an increase in the amount of hair on your pillow or brush can be disconcerting, mainly when it occurs regularly. Although some shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, excessive hair loss can sometimes be linked to medication, including spironolactone. Spironolactone is commonly prescribed for conditions like high blood pressure, heart failure, and hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It works as a blocker of androgens, male hormones that can contribute to hair thinning, particularly in women.
While spironolactone is recognized for its ability to prevent hair loss associated with hormonal imbalances, it may also cause temporary shedding in some individuals, particularly during the initial weeks of treatment. This occurs as the body adjusts to the medication, and hair follicles may enter the shedding phase before starting a new growth cycle. This shedding is temporary for most people, and hair regrowth resumes once the body achieves equilibrium. However, it’s essential to be aware that other factors, such as genetics, diet, and health problems, can also play a role in hair loss.
At Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County, we understand the challenges of hair loss, whether it’s caused by spironolactone or other factors. Our clinic offer a variety of solutions, including hair restoration treatments and products like Minoxidil (Rogaine), to help restore your confidence. We also consider how diet, stress, and underlying conditions like depression may impact your hair. Contact us today to schedule a consultation if you’re concerned about hair loss while taking spironolactone. Our doctors and dermatologists will assess your situation, review your health history, and create a personalized treatment plan to help you achieve a healthier, fuller head of hair.

Recent Comments