The Connection Between Dandruff and Hair Loss
Dandruff is a common scalp condition that causes flaking and itching of the scalp. While it is often considered a minor annoyance, dandruff can also lead to hair loss in some cases. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes of dandruff and how it can contribute to hair loss. We will also discuss how to treat dandruff and stop it from contributing to additional hair loss, as well as how NeoGraft hair restoration can assist you in regaining your hair.
Understanding Dandruff and Hair Loss
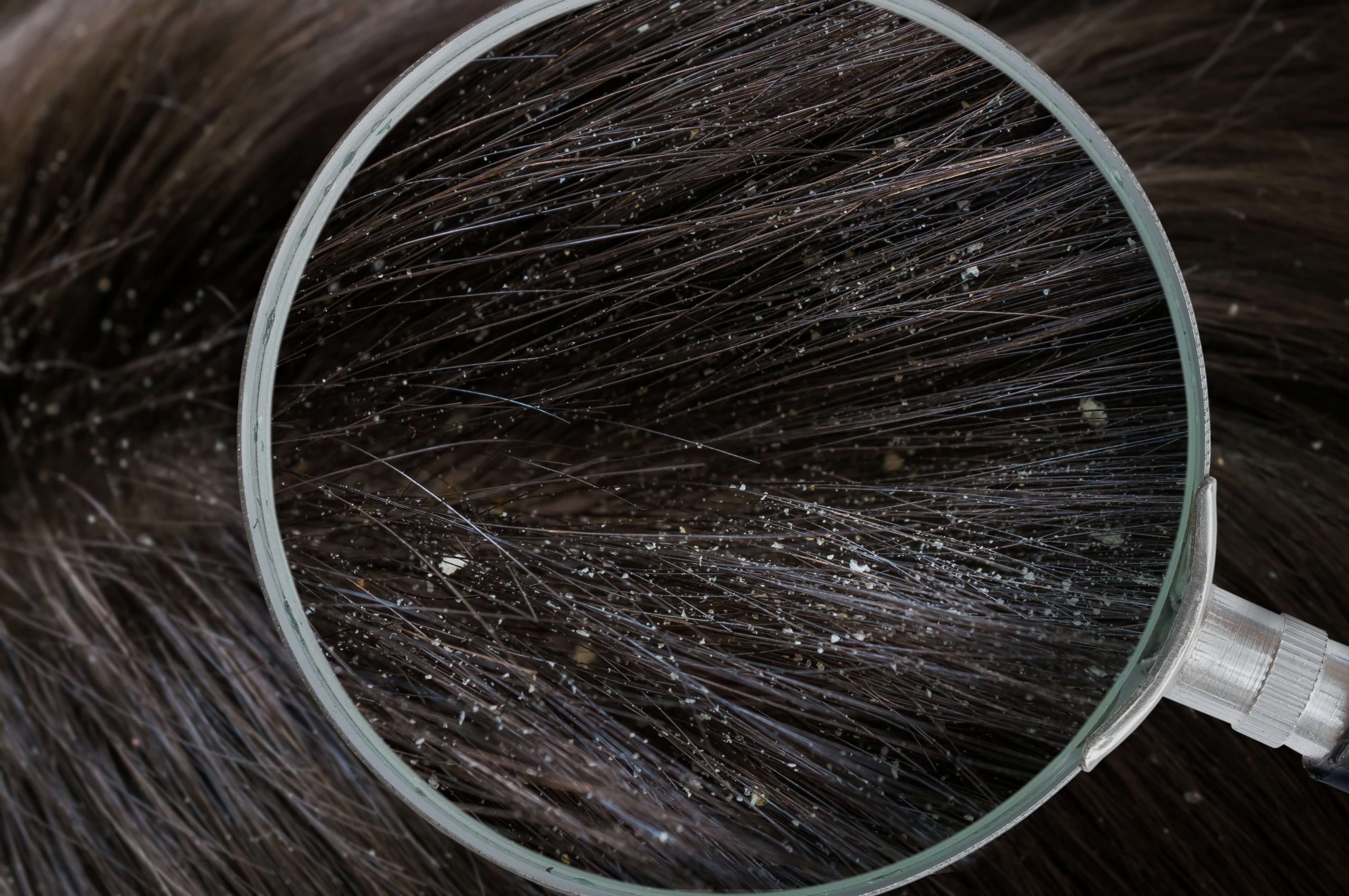

Dandruff on a patient in Newport Beach, California at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County
Dandruff, a common scalp condition characterized by flaking and potential itchiness, can be more than just a nuisance; it may also have implications for hair health and hair loss. While dandruff does not directly cause hair loss, the associated scratching due to itchiness can damage the hair follicles, indirectly affecting hair growth and potentially contributing to increased hair shedding. Scalp health is paramount for healthy hair growth, and conditions that disrupt the scalp’s balance, such as excessive sebum production or fungal infection, can exacerbate dandruff and hair shedding issues.
Furthermore, underlying issues often contribute to both dandruff and hair loss. Hormonal imbalances, for example, can lead to variations in sebum production, impacting both scalp health and hair vitality. Similarly, deficiencies in essential vitamins and nutrients can affect hair strength and scalp wellness, potentially leading to conditions like alopecia, an autoimmune disorder that causes baldness in severe cases.
A comprehensive approach that includes proper haircare is essential to manage dandruff and mitigate its potential impact on hair loss. This might involve using medicated shampoos designed to control dandruff and maintain scalp health, as well as natural remedies to balance scalp sebum production and reduce inflammation. Regularly cleaning the scalp and hair to remove build-up and adopting a diet rich in vitamins and nutrients essential for hair health can also help manage dandruff and minimize hair shedding.
The Link Between Dandruff and Hair Loss
The connection between dandruff and hair loss is often misunderstood, leading to misconceptions about their relationship. While dandruff primarily affects the scalp, causing it to become dry, itchy, and flaky, it can indirectly influence hair loss through several mechanisms. One of the primary concerns is the mechanical damage caused by scratching. Intense scratching in response to the itchiness of dandruff can damage hair follicles, leading to weaker hair roots and increased hair shedding. This mechanical disruption can exacerbate hair loss, particularly in individuals predisposed to hair thinning or baldness.
Another aspect of the link between dandruff and hair loss is the role of inflammation. Dandruff can lead to increased scalp inflammation, which, if left untreated, may harm the hair follicles and impair hair growth. Additionally, conditions that cause dandruff, such as seborrheic dermatitis, are often associated with abnormal sebum production. Excess sebum can clog hair follicles, hindering hair growth and contributing to hair loss.
Understanding the relationship between dandruff and hair loss highlights the importance of addressing scalp health as a component of overall haircare. Effective treatments may include products that reduce dandruff, control sebum production, and soothe scalp inflammation. In some cases, addressing hormonal imbalances and ensuring an adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals may also be beneficial in breaking the cycle of dandruff and hair loss. For those experiencing significant hair loss or scalp issues, consulting with a healthcare provider can offer tailored solutions and remedies to improve scalp health and reduce the impact of dandruff on hair loss.
Does dandruff cause hair loss?
It is unlikely that mild dandruff brought on by dry skin will result in hair loss or thinning. However, if you often pick or scratch your scalp to ease irritation or remove flakes, chronic dandruff may become another cause of losing hair. Thinning hair and hair loss can occur from over-scratching your scalp, leading to inflammation and possibly damage to the hair follicles.
Thankfully, additional hair loss caused by dandruff is typically a temporary issue. Hair usually grows back when treatment is completed, and the dandruff disappears. It is possible to reduce the risk of hair loss by fighting the impulse to pick and itch.
7 Symptoms of Dandruff
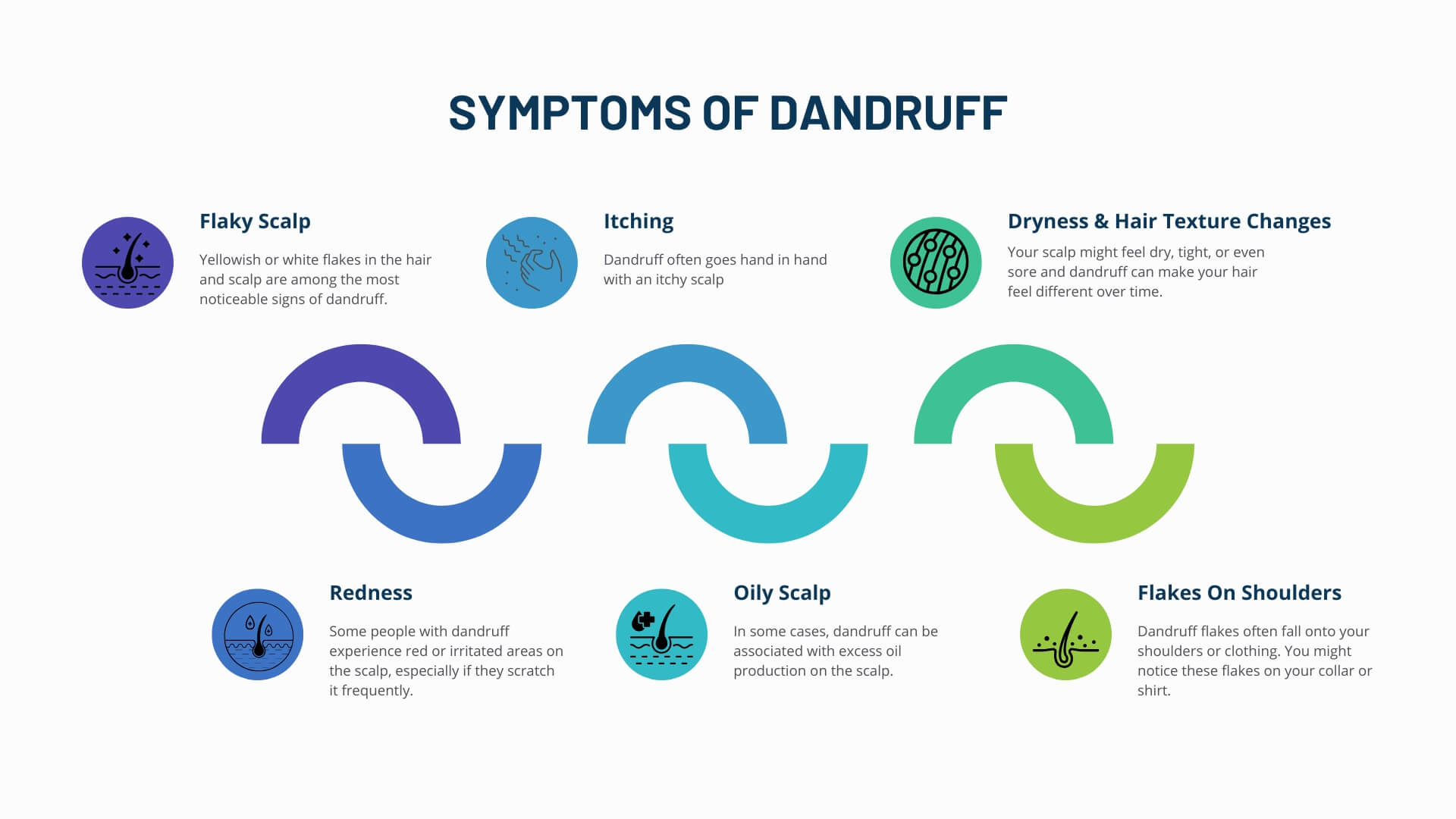
Symptoms of Dandruff in Newport Beach, California at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County
Dandruff is a common scalp condition that can be bothersome. You might notice a few telltale signs if you’re dealing with dandruff. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Flaky Scalp: Yellowish or white flakes in the hair and scalp are among the most noticeable signs of dandruff. These flakes can sometimes be noticeable on your clothing, too.
- Itching: Dandruff often goes hand in hand with an itchy scalp. You may be constantly scratching your head, which can be embarrassing and uncomfortable.
- Dryness: Your scalp might feel dry, tight, or even sore. This dryness can contribute to the flaking and itching.
- Redness: Some people with dandruff experience red or irritated areas on the scalp, especially if they scratch it frequently.
- Oily Scalp: In some cases, dandruff can be associated with excess oil production on the scalp. It might make your hair look greasy even though you have those flaky white bits.
- Flakes on shoulders: Dandruff flakes often fall onto your shoulders or clothing. You might notice these flakes on your collar or shirt.
- Hair Texture Changes: Dandruff can make your hair feel different over time. It may become dull, dry, or less manageable.
Some individuals may experience only a few of these symptoms, while others might have a combination of several. If you’re dealing with persistent dandruff and it’s bothering you, it’s a good idea to consult a dermatologist or a healthcare professional.
6 Causes Of Dandruff
Dry Skin:
Dry skin is the most common cause of dandruff. When the scalp is not properly hydrated, it can lead to dry, flaky skin. This can be caused by a number of factors, including weather changes, using harsh hair products, and not drinking enough water. If you have dry skin, you may also notice that your hair is dull and brittle.
Oily Skin:
Oily skin is another common cause of dandruff. When the sebaceous glands in the scalp produce too much oil, it can lead to an overgrowth of yeast on the scalp. This can cause the scalp to become red, itchy, and covered in flakes. In some cases, oily skin can also contribute to hair loss.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema, can cause dandruff. If you have one of these conditions, you’ll need to see a doctor for treatment.
Stress:
If you’re under a lot of stress, it can lead to dandruff. Be sure to manage your stress levels and get plenty of rest to help prevent this problem.
Dietary Issues:
If you don’t eat a balanced diet, it can lead to dandruff. Be sure to eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Also, drink plenty of water to keep your scalp hydrated.
Hair Care Products:
If you use hair care products that are too harsh, it can strip your scalp of its natural oils. This can lead to dandruff. Be sure to use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners. Also, avoid using hot tools such as curling irons and hair dryers.
Other causes of itchy, dry scalp and hair loss
While thinning hair is not usually caused by moderate dandruff or dry skin, hair loss and dry scalp coexist. Some reasons for hair loss and an itchy, dry scalp include the following.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis, also called seborrheic eczema, is a persistent scalp condition that manifests as the following symptoms:
- Dandruff
- Itchy scalp
- Red scalp
- Greasy skin patches with flaky, white scalp scales
- Scalp rashes
- Hair loss
- Thinning hair
Although the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis in some individuals is still unknown, the following factors may be involved:
- Weak immune system
- Malassezia yeast overgrowth
- Stress
- Genetics
- Certain medications
Hair loss caused by seborrheic dermatitis is typically reversible. In the afflicted area, hair growth will probably resume after the condition’s symptoms are managed.
Scalp psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder caused by the body producing new skin cells around the scalp too quickly. The following symptoms come from this:
- Plaques are thickened reddish skin areas.
- Dry scalp skin
- Silvery dandruff flakes
- Hair loss
Although the precise origins of scalp psoriasis are uncertain, immune system dysfunction is a contributing factor. Psoriasis of the scalp typically results in reversible hair loss. Hair growth may restart if outbreaks are contained.
Scalp ringworm
Scalp ringworm, an infection brought on by a fungus, may result in hair loss and dry scalp. It is an infectious disease transferred via intimate contact with an infected person. Children and teenagers are particularly prone to experience it because they share a cap, combs, and other hair accessories more frequently.
Scalp ringworm symptoms include:
- Scaly patches on the scalp
- Itching
- Patchy hair loss
- Scalp inflammation
- Pink skin
After the infection is treated, ringworm-related hair loss usually stops, and most patients have complete regrowth of hair in the afflicted area in three to six months.
How to Prevent Hair Loss From Dandruff?
There are a few things you can do to prevent hair loss from dandruff:
- Use a dandruff shampoo: Shampoos that contain zinc pyrithione or selenium sulfide can help to reduce the amount of dandruff on your scalp. Be sure to use these shampoos as directed, and avoid using them more than twice per week, as this can dry out your scalp and make the problem worse.
- Avoid irritants: If you notice that certain hair products or fabrics are causing your dandruff to flare up, avoid them if possible. This may mean switching to a different shampoo or conditioner or wearing loose-fitting clothing made from natural fibers.
- Keep your scalp clean: Regular shampooing can help to keep your scalp clean and free of dandruff-causing fungus and bacteria. Be sure to shampoo at least twice per week, and more often if you have an oily scalp.
- Use a medicated cream or gel: If over-the-counter shampoos don’t seem to be helping, talk to your doctor about using a stronger medicated cream or gel. These products are available by prescription only and can help to control severe dandruff.
- Try light therapy: In some cases, hair restoration doctors in Newport Beach may recommend a form of light therapy called photodynamic therapy. This treatment involves using a special lamp to expose your scalp to light. The light kills the fungus and bacteria that can cause dandruff.
Dandruff is a common scalp condition that affects people of all ages. Though it’s not usually serious, dandruff can be annoying and difficult to get rid of.
If you have dandruff, there are several things you can do to treat it and prevent it from coming back. With a little time and effort, you can say goodbye to those pesky flakes for good!
If you have an issue with hair loss, contact Dr. George Brennan at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County. We use cutting-edge Newport Beach hair transplant procedures to help you achieve your goals. To schedule a consultation, call us now.
FAQs: Can Dandruff Cause Hair Loss
1. What is dandruff?
Dandruff is a common scalp condition characterized by flaky, white, or yellowish scales on the scalp. It is often accompanied by itching, dryness, or redness. Dandruff can be caused by factors such as dry skin, excess oil production, or fungal infections.
2. What are the main symptoms of dandruff?
Symptoms of dandruff include visible flakes on the scalp and hair, itchiness, dryness, redness, oily patches on the scalp, and sometimes a change in hair texture. Flakes may also be noticeable on clothing.
3. What causes dandruff to develop?
Common causes include dry skin, overactive sebaceous glands producing excess oil, fungal infections like *Malassezia*, stress, dietary deficiencies, and harsh hair products. Medical conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis can also trigger dandruff.
4. Can oily scalp contribute to dandruff?
Yes, an oily scalp can lead to dandruff. Excess oil can promote the growth of yeast and fungi on the scalp, causing irritation, redness, and the formation of flakes.
5. What is the difference between dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis?
While dandruff is typically mild and involves flaky, itchy scalp skin, seborrheic dermatitis is a more severe form that includes greasy patches of skin, redness, and sometimes hair loss. Both conditions can share similar triggers, such as yeast overgrowth and excessive oil production.
6. How can dandruff be managed or treated?
Dandruff can be treated using medicated shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or ketoconazole. Additional strategies include maintaining a clean scalp, using gentle hair products, and avoiding triggers like harsh chemicals or stress.
7. Are there natural remedies for dandruff?
Natural remedies like tea tree oil, aloe vera, apple cider vinegar rinses, and coconut oil can help balance scalp health, reduce inflammation, and manage dandruff symptoms. However, effectiveness varies, and medical advice should be sought for severe cases.
8. Can stress contribute to dandruff?
Yes, stress can exacerbate dandruff by disrupting the skin’s natural balance, weakening the immune system, and increasing oil production, all of which can make the scalp more susceptible to dandruff.
9. Is dandruff contagious?
No, dandruff is not contagious. It is often caused by factors like scalp health, oil production, and susceptibility to fungal overgrowth rather than external transmission.
10. What should I do if over-the-counter products don’t work?
If over-the-counter shampoos and treatments fail to resolve dandruff, consult a dermatologist. They can recommend more robust medicated products, assess underlying causes, or suggest therapies like prescription creams, gels, or photodynamic therapy.
Related Posts
- Hair Restoration Statistics 2023
- Do Hair Transplants Really Work?
- What Are The Pros And Cons Of A Hair Transplant?
- Do Hair Transplants Last Forever?
- How to Stop Alopecia Areata From Spreading
- What is a Neograft Hair Transplant?
- Can Shampoo Cause Hair Loss?
- Beard and Facial Hair Transplants
- What’s the Difference Between Hair Shedding and Hair Loss?