Understanding Hair Transplant Effectiveness: Facts and Results
NeoGraft Hair transplants aim to stimulate hair growth in parts of the scalp that are bald and sparsely covered. These are effective treatments for various hair loss conditions but do not prevent further hair loss, and people could require further transplants for long-lasting outcomes.
In addition to being a typical result of aging, thinning and hair loss may also be induced by a medical condition and trauma toward the scalp. When encountering hair loss, some people get a hair transplant for reconstructive or cosmetic purposes.
In this article, we examine the success rates of several hair transplant procedures, their duration, and possible side effects.
Do hair transplants really work?
Generally speaking, Orange County hair transplants are more effective than over-the-counter hair restoration solutions. But there are a few things to think about:
- In an estimated 3 to 4-month period, anywhere between 10 and 80 percent of transplanted hair would fully return.
- The transplanted hair may thin over time, just like natural hair does.
- Although plasma therapy may help up to 75% or more of such transplanted hairs entirely regrow, those with inactive hair follicles (sacs beneath the skin that typically contain hair but no longer generate hair) may have fewer successful transplants.
Some people do not benefit from hair transplants, and they are primarily used to regrow hair in cases where it’s gone due to an injury, baldness, or thinning naturally.
They perform the majority of transplants using your current hair, which makes them less successful in treating people who have:
- a widespread pattern of baldness and thinning
- hair loss brought on by chemotherapy and other medications
- wounds that left extensive scars on the scalp
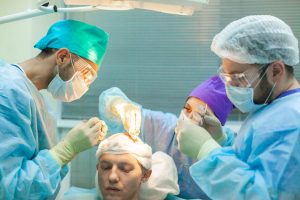
How does a hair transplant work?
A hair transplant in Orange County involves taking the hair you currently have and transplanting it to an area that is currently bald. Although it usually comes from the back of the head, it can come from anywhere else on your body.
Before the transplant, your surgeon sterilizes the location of the hair extraction and numbs it with a topical anesthetic. You can even ask for medication if you want to doze off throughout the treatment.
After that, your doctor will use the FUT or FUE hair transplant procedure.
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT)
Sometimes, FUT (FUSS) is called follicular unit strip surgery. Your surgeon will carry out a FUT operation by doing the following:
- A portion of your scalp is cut out by the surgeon from the back of the head using a scalpel. The strip can span from ear to ear and usually is 6 to 10 inches long.
- After removing the scalp, the region is stitched closed.
- The scalpel cuts the scalp strip into smaller pieces by the surgeon and their assistants. The resulting composition can be divided into 2,000 smaller pieces or grafts, containing just one hair each.
- The surgeon creates tiny holes within the scalp wherein hair will be transplanted utilizing a needle or blade.
- The surgeon inserts hairs from the removed scalp tissue into the puncture holes. This process is called grafting.
- Gauze or bandages are applied to cover the surgical sites afterward.
The determination of the particular amount of grafts depends on the following factors:
- the type of your hair
- the transplant site’s size
- hair quality (thickness)
- hair color
Follicular unit extraction (FUE)
Your surgeon follows these procedures to carry out an FUE procedure:
- On your head’s back, surgeons shave your hair.
- Next, the surgeon removes a few hair follicles from the scalp, and each extraction leaves tiny marks.
- The surgeon cuts tiny holes in your scalp, similar to the FUT operation, and inserts hair follicles into those holes.
- Covering the surgery site with gauze or bandages followed.
Success rates
Newport Beach Hair transplants are successful treatments for restoring hair growth following various causes of hair loss. The expertise and knowledge of the surgeon and the patient’s donor hair’s thickness are two essential elements that can impact the success rate following hair transplant surgery.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) claims that hair transplantation can slightly alter hair fullness. Individuals may opt for skin flap surgery, tissue expansion, or scalp reduction techniques for more pronounced modifications.
There are no substantial studies that provide exact success rates for hair transplants. Nonetheless, several smaller studies and papers offer some details regarding the efficacy of these methods.
According to this study, most patients who underwent the FUE method using scalp hair in addition to body or beard hair were pleased with the outcomes after an average follow-up of 2.9 years. The mean overall satisfaction rating for the 79 participants was 8.3 out of 10.
According to a different study, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy combined with FUE improves the outcome of FUE hair transplants. The PRP group’s subjects experienced over 75% hair regrowth in six months. Compared with people in the non-PRP group, they experienced faster skin repair and hair density gains.
Recovery
FUT and FUE can be finished in a few hours to many days, which partially depends on the surgeon’s level of effort. On the day of the procedure, you will leave for home.
After the procedure, the surgeon gently removes the existing bandages. Your surgeon may inject triamcinolone into the region to lessen any swelling that may be present.
After the surgery, you may experience pain or irritation in the transplant site and the area where hair removal occurs. In the following days, your surgeon may recommend the following:
- prescription medications like ibuprofen (Advil)
- Antibiotics to stop infections
- anti-inflammatories to reduce swelling, including an oral steroid
- Take drugs like finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) to encourage hair growth.
Here are some tips for post-hair transplantation care:
- Give yourself a few days before washing your hair following the procedure. Throughout the first few weeks, use gentle shampoos.
- In around three days, you should be ready to resume your job or other regular activities.
- Avoid using a comb or brush on the fresh grafts for around three weeks.
- Avoid wearing headgear, pullover shirts, or jackets until your doctor gives the all-clear.
- Stop working out for about a week.
When some hair falls out, don’t be concerned. It is a stage in the procedure. For a few months, transplanted hair might grow slowly or blend in with the surrounding hair flawlessly.
Do hair transplants last?
Most of the time, a person with a successful hair transplant will have hair that looks thicker. After the surgery, however, people can still experience hair loss and thinning, which could make their hair look unnatural or spotty. They might need several transplants in the future for results that persist longer.
There is a possibility that a number of the transplanted hair follicles won’t “take,” according to the ASPS. There is no new hair growth after these follicles die.
The ASPS also cautions people to expect the possibility of a “touch-up” procedure. This technique can help by merging the follicles to give a more natural appearance or filling in places that aren’t thick enough.
Follow the post-procedure instructions provided by your surgeon for the best results. By doing this, they will have a better chance of having an effective hair transplant. A person might have to refrain from exercise and strenuous activity for a few weeks, and they might have to hold off on washing their hair for a few days.
Hair Transplant Side Effects
According to the ASPS, hair transplants in Orange County generally remain safe when done by a trained, experienced surgeon. Unfortunately, some adverse effects can occur even in successful hair transplant work.
Bleeding or Infection
Making incisions or cuts in the skin is necessary for hair transplants. A surgeon makes a small incision on the scalp to insert the donor follicles after removing the donor follicles with an incision. There is a chance of infection and excessive bleeding with every incision.
Scars
Scarring could potentially occur in the transplant area as well as the donor area. Before deciding to have the operation, a person should discuss these risks with their surgeon.
When using the FUSS technique, the surgeon usually creates a long, linear scar where it removes a section of the scalp. As fresh hair grows around the scar, it might blend in. Nonetheless, it may be noticeable if it widens while healing, its surrounding hair gets thin, or the person keeps their hair short.
The FUE procedure may also leave minor scars in the region where the doctor removed the follicles with a punch device. Yet, these scars might not be as evident as the FUSS scar.
The area around its transplanted hair may develop raised bumps in some circumstances, and hair regrowth could hide these bumps.
Swelling and pain
Following treatment, some people may feel pain while their skin recovers. To assist patients with this, they could receive painkillers from their surgeon. When the skin heals, the face and head may also have considerable swelling.
Who is most likely to benefit from a hair transplant?
Doctors typically recommend hair transplant surgery Orange County for individuals experiencing hair loss or thinning hair who want to restore their hairline or improve their hair density.
The following are some examples of individuals who may benefit from a hair transplant:
- Men with male pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition that causes hair loss in men. Newport Beach Hair transplant surgery can be an effective solution for men with male pattern baldness who have a stable donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) with sufficient hair follicles for transplantation.
- Women with female pattern hair loss. While less common than in men, women can also experience hair loss due to female pattern hair loss, characterized by thinning hair on the crown of the scalp. Women with this condition who have good donor hair can also benefit from a hair transplant.
- Individuals with hair loss due to trauma or scarring. Hair transplant surgery can also benefit individuals who have experienced hair loss due to trauma, such as burns, accidents, or scarring from previous surgeries. Transplanted hair follicles can help to restore hair in the affected areas and improve the appearance of scars.
- Individuals with thinning eyebrows or eyelashes. Hair transplant techniques can also restore thinning or absent eyebrows or eyelashes due to genetic factors, trauma, or medical conditions. Transplanted hair follicles can create a natural-looking appearance for eyebrows and eyelashes.
- Individuals with hair loss due to medical conditions. Certain medical conditions such as alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss, or traction alopecia, caused by tension or pulling on the hair, may benefit from hair transplant surgery. However, the underlying cause of hair loss should be addressed and stabilized before considering a hair transplant.
It’s important to note that only some are suitable candidates for a hair transplant. A thorough evaluation by a qualified and experienced hair restoration specialist in Orange County is necessary to determine the best treatment approach for each individual.
Is a hair transplant permanent?
Yes, a hair transplant is generally considered a permanent solution for hair loss. Surgery to transplant hair entails removing hair follicles from one part of the body (commonly the back of the head, where hair is usually denser) and transplanting them to an area with thinning or no hair (such as the front of the scalp or the crown). After the transplanted hair follicles have established a blood supply and have grown in their new location, they are expected to continue to grow and behave like the hair from the donor area.
It’s important to note that while hair transplant surgery can provide long-lasting results, the procedure’s success can depend on various factors, including the quality and quantity of the donor’s hair, the skill and experience of the surgeon, and the overall health and healthy lifestyle of the patient.
Hair loss can be progressive, and even after a successful hair transplant, further hair loss may occur in untreated areas of the scalp. Further treatment or maintenance might be necessary to maintain the desired results. It’s advisable to consult with a qualified Newport Beach hair restoration specialist to discuss your case and expectations.
A hair transplant can be a permanent solution for hair loss, but it’s essential to consider all factors and realistic expectations before undergoing the procedure.
Conclusion
Hair transplant surgery could be a viable option for people with hair loss and hair thinning. Although it might not be a long-term fix for thinning hair, it can often help many people regain their confidence and hair fullness.
Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County is here if you are considering hair transplantation surgery. Our clinic offers hair restoration techniques and other options that suit your case. Call us at (949) 644-1641 or schedule an appointment or consultation.
FAQs: Do Hair Transplants Really Work
1. What is a hair transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of your body (often the back of the head) to areas where hair is thinning or absent. This process can help restore hair to bald or thinning areas.
2. How long does it take for transplanted hair to grow?
Transplanted hair typically begins to grow back 3 to 4 months after the procedure, with most of the hair fully regrowing within this time frame. However, the rate of hair growth can vary depending on the individual.
3. Is a hair transplant permanent?
Yes, hair transplants are generally considered permanent. The transplanted hair follicles are taken from an area with healthy hair and are expected to grow for the rest of your life. However, further hair loss in untreated areas may require additional treatments.
4. What are the types of hair transplant procedures?
The two main methods are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). In FUT, a strip of the scalp is removed and divided into smaller grafts, while FUE involves extracting hair follicles from the donor area and transplanting them.
5. What are the risks of hair transplant surgery?
Hair transplants carry risks like any surgery, including infection, bleeding, scarring, and swelling. Some people may also experience pain or irritation after the procedure. For optimal healing, it’s important to follow post-surgery instructions.
6. Who is a good candidate for a hair transplant?
Ideal candidates for a hair transplant are those experiencing male or female pattern baldness, hair loss due to trauma, or thinning in areas like the eyebrows or eyelashes. A thorough evaluation by a hair restoration specialist is necessary to determine eligibility.
7. How long does the recovery take after a hair transplant?
Recovery time varies, but most individuals can resume activities within 3 to 5 days. The scalp may take a few weeks to heal fully. After the procedure, you should avoid intense physical activity for about a week.
8. Are there any side effects of hair transplants?
Common side effects include mild swelling, scarring, pain, and temporary hair shedding in the transplanted area. To minimize complications, it is essential to follow your surgeon’s aftercare guidelines.
9. Can hair transplants be combined with other treatments?
Yes, hair transplant procedures can be enhanced by treatments like Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, which stimulates hair growth and can improve the outcome and speed up recovery.
10. Will the transplanted hair thin over time?
While transplanted hair can grow thick and healthy initially, like natural hair, it may thin over time. Regular maintenance or additional transplants may be required to maintain the desired results.
Related Posts
- Hair Restoration Statistics 2023
- What is a Neograft Hair Transplant
- What Are The Pros And Cons Of A Hair Transplant?
- Do Hair Transplants Last Forever?
- How to Stop Alopecia Areata From Spreading
- Can Dandruff Cause Hair Loss?
- Can Shampoo Cause Hair Loss?
- Beard and Facial Hair Transplants
- What’s the Difference Between Hair Shedding and Hair Loss?