Smoking has long been recognized as a leading cause of many health issues, but one area where its impact is often overlooked is hair loss. Hair thinning, baldness, and a range of other hair-related conditions like alopecia can be exacerbated by smoking. Tobacco use, in particular, is linked to increased breakage and brittleness of hair. While smoking is widely understood to have detrimental effects on the lungs and heart, its effects on the scalp and hair follicles are just as significant. Studies have shown that cigarette smoking can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and weakening of the hair structure. This can cause hair loss and affect the scalp’s skin, making it more prone to damage. An article on the effects of smoking would highlight these issues, emphasizing the connection between smoking and deteriorating hair health.
In this post, we’ll explore the relationship between smoking and hair loss, mainly focusing on how smoking impacts hair follicles, blood flow, and overall hair health. Study findings show that smoking can lead to significant hair thinning and follicle damage. We’ll also discuss prevention methods, treatments, and what you can do to mitigate the damage caused by smoking.
Smoking and Its Impact on Hair Health
The effects of smoking on hair loss are increasingly being supported by scientific research. One of the primary ways smoking contributes to hair loss is through the harmful chemicals and toxins introduced into the body by cigarettes. Nicotine, a known vasoconstrictor, reduces blood flow by constricting blood vessels, including those that supply the scalp. Mechanisms involving other factors, such as oxidative stress and inflammation, contribute to this process. The onset of hair loss can be further accelerated by smoking-related damage to scalps and hair follicles. When blood flow is restricted, it limits the oxygen and nutrients delivered to hair follicles, impairing their ability to grow hair properly. The resulting damage also compromises the effectiveness of specific products designed for hair health. In some cases, medications intended for hair regrowth may not work as effectively due to the reduced blood flow caused by smoking.
Hair follicles are tiny organs in the scalp responsible for producing hair. They rely on a constant supply of nutrients to maintain healthy hair growth. However, smoking disrupts this process by decreasing circulation, meaning hair follicles receive fewer essential nutrients like oxygen, proteins, and vitamins crucial for hair health. The effect of reduced circulation has a direct correlation with hair loss as the degree of damage to hair follicles increases. This disruption also impacts the systems that regulate hair growth, making it harder for follicles to function correctly. There is a clear association between smoking and hair thinning, with some studies showing that smokers experience more significant hair loss. Tips for mitigating this damage include improving circulation through lifestyle changes, though the vertex of hair loss may still be impacted due to the continued reduction in nutrient supply.
Several studies have shown that smoking may contribute to hair thinning, where hair gradually becomes weaker and shorter. Over time, smoking accelerates the natural aging process of hair follicles, leading to premature baldness. These effects are even more noticeable in men, who tend to experience balding patterns (such as receding hairlines or thinning crowns) at an earlier age. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke directly impact the health of hair follicles, making them more susceptible to damage and premature aging.
The Role of DNA and Inflammation
Smoking causes DNA damage at a cellular level, which impacts the normal functioning of hair follicles. This damage is primarily due to the chemicals in cigarette smoke, which produce harmful free radicals in the body. These molecules cause oxidative stress, which damages cells and disrupts their normal functions. The oxidative stress from smoking damages the DNA inside hair follicle cells, impairing their ability to regenerate and produce healthy hair. According to theory, the chances of this damage leading to permanent hair loss increase with prolonged exposure to cigarette smoke. Studies suggest that cytokines and their release play a role in the inflammation and cell damage caused by smoking. Additionally, pollution from cigarette smoke can contribute to a compounded effect, further damaging hair follicles and increasing the risk of hair thinning.
As a result, the hair growth cycle is disrupted, leading to hair follicles entering a prolonged resting phase. This means that hair cannot grow at its usual rate, and some follicles may even stop producing hair. Additionally, smoking triggers chronic inflammation in the scalp, which further impairs the function of hair follicles and accelerates hair loss. One of the reasons for this is the reduced retention of nutrients and oxygen in the scalp due to restricted blood flow from tobacco smoke. This not only affects the scalp’s health but also leads to a reduced ability to repair damage. In some cases, patients seeking treatment in the UK may need to make an appointment with a specialist to address these issues and explore options for reversing hair loss.
Smoking and Hair Loss in Women
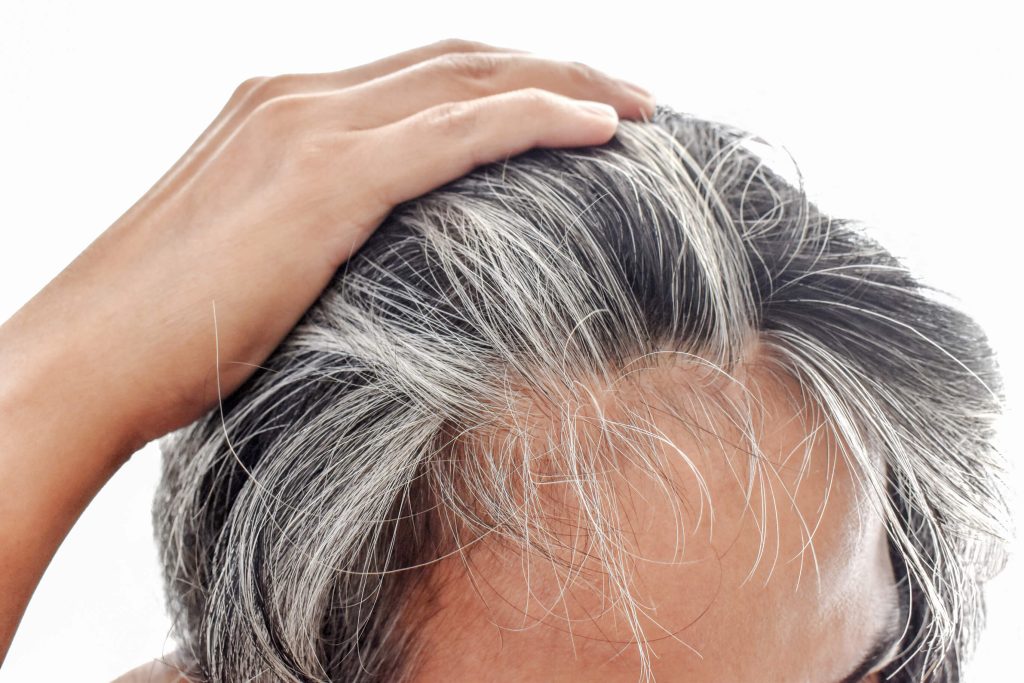

Understand the link between smoking and hair loss at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County California.
While hair loss due to smoking is often associated with men, women are also at risk. Women who smoke may experience more severe forms of hair loss. Research indicates that women smokers have a higher likelihood of developing thinning hair compared to non-smokers. The harmful effects of smoking on hair health are thought to be compounded by the hormonal changes that women go through, especially as they age. Evidence from studies involving mice has shown that smoking causes an imbalance in the scalp’s microvasculature, which refers to the small blood vessels that supply the hair follicles. This disruption leads to microinflammation, further impairing the follicles’ ability to function correctly and contributing to increased hair loss in women.
Nicotine, combined with other chemicals in cigarette smoke, can exacerbate the natural hormonal imbalances that women face as they enter menopause or experience another stage of life. This further damages hair follicles, increasing the risk of alopecia and other hair loss conditions. Hair restoration for women has become an increasingly sought-after solution to address these concerns. A literature review has shown that smoking affects receptors involved in hair growth, influencing the balance of key proteins responsible for hair follicle health. Hydroxylation and its inhibition have been linked to this process, affecting hair regeneration. These aspects highlight the associations between smoking and severe hair loss in women, making them more vulnerable to thinning and baldness.
How Smoking Affects the Hair Growth Cycle
The hair growth cycle consists of three primary stages: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). Damages caused by smoking to the blood vessels reduce circulation to the scalp, which decreases the amount of oxygen and nutrients that reach the hair follicles. Without proper nourishment, hair follicles enter the resting phase prematurely, which leads to increased shedding and hair thinning. Consulting a doctor may help determine the best course of action to address smoking-related hair loss. In addition, maintaining a balanced diet can help combat the nutritional deficiencies that may be exacerbated by smoking. Within the broader community, many smokers seek advice on ways to prevent hair loss, though they must be aware of the types of side effects that smoking has on overall hair health.
Studies suggest that smoking prolongs the telogen phase, causing hair to remain dormant for more extended periods. This results in delayed or stunted hair regrowth. For people who already have thinning hair or early signs of balding, smoking exacerbates the problem by accelerating hair loss. One example is the accelerated hair graying often seen in smokers. Smoking also triggers cravings for cigarettes, which can lead to further illness and health complications. The long-term illnesses caused by smoking can affect overall well-being, including hair health. Understanding your rights when seeking treatment options is essential, and gathering reliable sources can help you make informed decisions about therapies available for reversing hair loss.
The Impact of Nicotine and Cigarette Smoke on Blood Flow
Nicotine is one of the main culprits in reducing blood flow to the scalp. When blood vessels constrict due to nicotine’s effects, the scalp lacks the oxygen and nutrients essential for healthy hair growth. Proper circulation is key to supporting the growth of new hair, and smoking prevents this.
Additionally, cigarette smoke contains thousands of chemicals, including tar and carbon monoxide, which can further damage the small blood vessels in the scalp. This contributes to poor circulation, which impairs hair follicle function and slows the hair growth cycle. Over time, this leads to a noticeable reduction in hair density and overall health.
Risk Factors for Hair Loss in Smokers
While smoking itself is a significant factor in hair loss, other risk factors increase the likelihood of smoking-related hair damage. These include:
- Age: As people age, their hair follicles weaken and produce less hair. Smoking accelerates this process, especially in individuals who are already at an advanced age.
- Genetics: If you have a family history of hair loss, smoking can worsen the condition. Individuals with a genetic predisposition to alopecia or male/female pattern baldness are more likely to experience significant hair loss when smoking.
- Stress: Smoking is often associated with higher levels of stress, which can directly contribute to hair loss. Stress can cause telogen effluvium, in which many hair follicles enter the resting phase, resulting in excessive shedding.
Prevention and Treatment Options
If you’re a smoker and you’re concerned about hair loss, the most crucial step is to quit smoking. Smoking cessation can significantly improve circulation to the scalp, reduce inflammation, and allow hair follicles to receive the nutrients they need for healthy growth. While quitting smoking can be challenging, it’s one of the most effective ways to prevent further damage to your hair.
In addition to quitting smoking, several other treatment options are available for people experiencing hair loss. One of the most widely recommended treatments is Minoxidil, an over-the-counter medication that stimulates hair regrowth. Minoxidil is available in topical solutions and foam forms and has been proven to help slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth in many individuals.
For those with more advanced hair loss, Neograft for Women and Men Hair Loss Prevention treatments offer a more permanent solution. Neograft is a minimally invasive procedure that uses follicular unit extraction (FUE) to transplant healthy hair follicles into thinning areas of the scalp. Neograft has become a popular choice for both men and women looking to restore their hairline or improve overall hair density.
Hair Transplant Treatments and Timelines
A hair transplant may be a suitable option for individuals who have lost significant amounts of hair due to smoking or other factors. Hair transplant timelines vary depending on the method used and the extent of hair loss. After a hair transplant procedure, it typically takes several months for new hair to begin growing. The full results may not be visible until 9-12 months after the procedure, and the healing process can take time.
It’s essential to have realistic expectations about the results of a hair transplant. The procedure can provide significant improvements, but depending on your hair loss, multiple sessions may be needed for optimal results.
Does Vaping Cause Hair Loss?
With the rise of vaping as a smoking alternative, many people are wondering whether it, too, has an impact on hair health. While the research on vaping and hair loss is still limited, it’s reasonable to assume that vaping may have similar effects on hair follicles due to the presence of nicotine in e-cigarettes. Nicotine reduces blood flow to the scalp, just as it does when smoking traditional cigarettes.
Although more studies are needed to understand the link between vaping and hair loss fully, it’s safe to say that vaping is not a completely safe alternative when it comes to preserving your hair health.
Conclusion
The link between smoking and hair loss is clear: smoking accelerates the aging of hair follicles, reduces blood flow to the scalp, and promotes inflammation that disrupts the normal hair growth cycle. Whether you’re a smoker or someone concerned about hair loss, it’s essential to understand the impact of smoking on your hair health.
If you’re experiencing hair thinning or early signs of balding, consider exploring treatment options at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County. Remember, quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in improving your hair’s health. Don’t wait for hair loss to become a more significant issue—seek professional advice and take steps to prevent further damage to your hair.
If you’re interested in more information about hair transplant timelines, how many hair transplants a person can have, or signs of balding at 20, consider contacting or scheduling a consultation with a hair restoration specialist. Your hair health is essential, and treatment options are available to help you restore your hairline and regain confidence.













Recent Comments