Pregnancy is a time of great joy and excitement, but it also comes with many changes to a woman’s body. One of the most common concerns women experience during pregnancy is hair loss or changes in their hair’s texture. While pregnancy-related hair changes are entirely regular, they can sometimes be unsettling. Many women want to understand why these changes happen, how to manage them, and what treatments or remedies are available. In this blog, we will explore the causes of pregnancy-related hair loss and the hormonal and lifestyle factors involved and provide expert insights into managing hair health during pregnancy. Proper use of conditioner and shampoo can help maintain balance in hair while knowing the amount of care needed and the right products for your hair type is essential. Understanding this information will aid in managing your hair effectively during this period of change.
Understanding Hair Loss During Pregnancy
Hair loss during pregnancy is more common than many realize. About 40-50% of women experience some form of hair shedding or thinning during pregnancy. While this may seem alarming, it is typically temporary and often resolves after birth. Pregnancy-related hair loss can occur during any trimester, with some women experiencing it earlier than others. Skin changes during pregnancy can also impact the hair’s health, making it more susceptible to thinning patches. While this may be concerning, it is often temporary and not a cause for alarm. In many cases, hair loss is associated with the hormonal changes of pregnancy, and breastfeeding can sometimes contribute to continued shedding. However, anything outside of typical pregnancy symptoms should be addressed with a doctor.
Hormonal changes, particularly the increase in estrogen during pregnancy, play a significant role in this process. Estrogen promotes the hair growth phase, helping to maintain a thicker, fuller head of hair. However, estrogen levels drop rapidly after delivery, and many women may experience hair shedding. This state change can lead to a hormonal imbalance that contributes to hair loss. Understanding the sources of these hormonal fluctuations is essential in managing the transition. During pregnancy, the body is focused on supporting the child and adjusting to new life stages. While these changes are natural, some women may seek beauty treatments to address hair thinning. Understanding this cycle is crucial in managing and coping with pregnancy-related hair changes.
The Impact of Hormones on Hair Growth
Pregnancy triggers significant hormonal changes that affect many aspects of a woman’s body, including hair. Estrogen, a hormone that is elevated during pregnancy, is responsible for extending the hair growth phase, which in turn helps the hair grow thicker and longer. Many women notice that their hair appears fuller and healthier during pregnancy, with less shedding than usual. However, the sudden shock to the body can disrupt this process after childbirth. Women may sometimes experience traction alopecia due to changes in hair care practices or styles. Additionally, the body’s decreased oxygen levels during pregnancy and postpartum and potential issues like constipation can further impact hair health. On average, these changes are temporary and resolve as the body adjusts.
However, the flip side is that estrogen levels drop drastically after childbirth, signaling the hair follicles to shed the hair accumulated during the pregnancy. This is why many women experience significant hair loss during the postpartum period. The sharp decrease in estrogen causes a higher-than-normal number of hair follicles to enter the shedding phase, resulting in noticeable hair thinning and shedding. This happens for many reasons, including hormonal shifts, stress, and other factors. Times of significant change, like childbirth, often lead to these changes in the body. The development of the hair cycle during pregnancy leads to temporary signs of fullness, but after delivery, shedding begins. It’s important to understand that these changes are regular and not permanent. Many women share their experiences and things they tried to help with hair loss on platforms like Instagram, offering tips for managing hair changes. This is a common issue with managing rights, and everyone’s experience will vary.
Stress and Pregnancy-Related Hair Loss
Stress is another significant factor contributing to hair loss during pregnancy. Pregnancy’s mental and emotional demands, combined with the physical stress of carrying a baby, can lead to increased hair shedding. Stress-induced hair loss is often a result of telogen effluvium, where the body’s response to stress causes hair follicles to enter the resting phase prematurely. As a result, hair shedding increases, leading to noticeable thinning or patchy hair loss. In some cases, stress can also exacerbate conditions like alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder that causes patches of hair loss. In addition to stress, experiencing a miscarriage can further disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, contributing to additional shedding. Thanks to the various treatments available, many women see improvement over time. While hair loss can affect men and women, pregnancy-related hair shedding is specific to women’s hormonal changes, making it a unique experience.
Managing stress during pregnancy is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Activities like prenatal yoga, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can help lower stress levels and support a healthier hair growth cycle. In some cases, stress can also trigger conditions like hypothyroidism, which affects hormone levels and can lead to further hair loss. This can make it more difficult for people to manage their hair health. While there is no immediate cure for stress-induced hair loss, treatments like minoxidil and other topical solutions may help promote regrowth. Additionally, severe trauma during pregnancy can exacerbate hair shedding, making it essential to take care of both mental and physical health during this time.
Nutritional Imbalances and Pregnancy Hair Loss
A woman’s diet plays a vital role in hair health, and pregnancy places additional nutritional demands on the body. Pregnant women need higher levels of specific vitamins and minerals, including folic acid, iron, biotin, and vitamin D. A lack of these essential nutrients can cause hair follicles to weaken, leading to hair thinning and shedding. Additionally, conditions like hyperthyroidism can increase the risk of hair loss, and fatigue from hormonal fluctuations can further affect hair health. Some women may also experience morning sickness, impacting their appetite and nutrient intake. Wearing ponytails too tightly can also stress the hair follicles, significantly contributing to hair thinning if nutrient levels are already compromised.
For example, iron deficiency is a common concern during pregnancy. Insufficient iron levels can impair the hair growth cycle, leading to hair loss at the root of the hair follicles. Similarly, a lack of biotin or vitamin D can affect the health of the hair follicles and contribute to hair thinning. Research has shown that these deficiencies can significantly impact hair health. Women should consult with their healthcare providers for personalized nutritional guidance and consider taking pills to ensure they are getting the essential nutrients needed for optimal hair growth. The right combination of vitamins can be crucial in maintaining a healthy scalp and preventing hair loss. When exploring options for hair care, it’s essential to evaluate the content of the products being used, ensuring they align with the individual’s needs. Some may also choose to incorporate natural remedies or products with trusted health brands’ logos.
A balanced diet that includes nutrient-dense foods like leafy vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains is crucial for supporting hair health during pregnancy. At the beginning of pregnancy, many women experience nausea, which can make it challenging to maintain a proper diet. To help combat this, women can incorporate small, frequent meals that include healthy fats, proteins like eggs, and complex carbohydrates. Prenatal vitamins, specifically designed to meet the increased nutritional needs of pregnant women, can also help ensure that the body is getting the proper nutrients for hair growth. Taking the right amounts of vitamins and minerals is essential for supporting the mother’s and baby’s health. A well-rounded approach, including proper diet and supplementation, can significantly affect the body’s ability to grow healthy hair during pregnancy. Many women find support from a team of healthcare professionals who guide them through these changes, offering advice on managing symptoms like nausea while maintaining overall health.
The Role of Genetics in Pregnancy Hair Loss
While hormones and diet play a significant role in pregnancy-related hair loss, genetics can also impact how a woman experiences hair changes during pregnancy. Women with a family history of hair thinning or loss may be more prone to experiencing similar issues during pregnancy. Additionally, genetic factors can influence the severity of hair loss and the speed at which hair grows after childbirth.
Suppose your mother or grandmother experienced significant hair loss during pregnancy. In that case, it may be helpful to consult a healthcare professional to understand your potential risks better and plan for managing hair health.
Postpartum Hair Shedding and Recovery
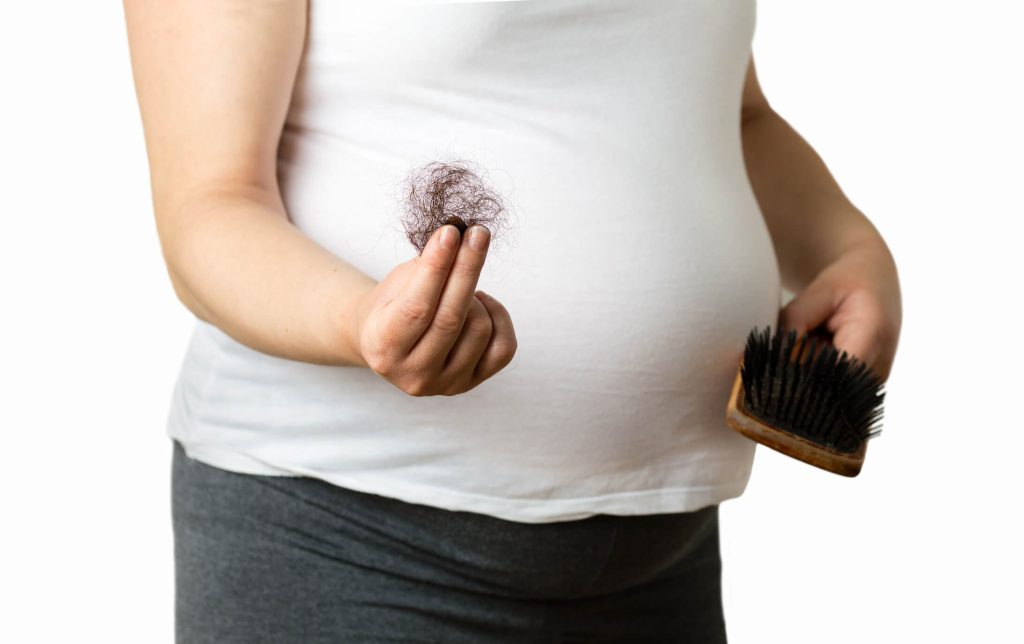

Hair loss during pregnancy is manageable with expert care and advanced solutions from Neograft Hair Restoration in Orange County California.
While hair loss during pregnancy can be concerning, it is essential to remember that it is usually temporary. After childbirth, many women experience what is known as postpartum shedding. This is a normal process where the hair retained during pregnancy due to elevated estrogen levels begins to shed as estrogen levels drop. The shedding typically begins three to six months after childbirth and lasts several months. However, this hair loss is generally not permanent, and hair growth usually returns to normal within a year.
Postpartum hair shedding can be incredibly distressing for new mothers, as they are already adjusting to the demands of caring for a newborn. However, with proper care, nutrition, and patience, hair typically returns to its pre-pregnancy thickness and fullness once the hormones stabilize.
Treatments and Remedies for Pregnancy-Related Hair Loss
While pregnancy-related hair loss is usually temporary, several treatments and remedies can help support healthy hair growth and minimize shedding. Here are some expert recommendations:
1. Healthy Diet and Supplements
Eating a balanced diet that includes essential vitamins and minerals is one of the most effective ways to support hair health during pregnancy. Iron, biotin, vitamin D, and folic acid are vital for hair growth. Taking prenatal vitamins as your doctor recommends can help fill nutritional gaps and promote stronger, healthier hair.
2. Hair Care Products
Gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners can help nourish the scalp and improve hair health. Look for products containing biotin, keratin, and antioxidants to promote healthy hair growth. Avoid harsh chemicals or heat-styling tools that can further damage the hair.
3. Stress Management
Managing stress during pregnancy is essential for overall health, including hairs health. Stress-reducing activities such as prenatal yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises can help regulate cortisol levels, which may reduce the impact of stress on hair growth.
4. Postpartum Hair Care
Many women experience postpartum shedding after delivery. While this is a natural process, proper hair care can help minimize further hair loss. Using lightweight hair products, avoiding tight hairstyles that pull on the hair, and gentle scalp massages can promote blood flow to the hair follicles and support recovery.
5. Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you experience severe or persistent hair loss during pregnancy or after childbirth, it is essential to consult with a doctor or dermatologist. A healthcare professional can evaluate your hormonal levels, assess your overall health, and recommend appropriate treatments such as topical solutions or hair transplants if necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Hair Transplant Timeline?
Hair transplant procedures typically take several months to show visible results. New hair follicles grow in stages, and it can take up to a year to see the full effects.
2. What Are Some Common Hair Loss Myths?
One common myth is that frequent washing or cutting of hair causes hair loss. Hair loss is typically due to genetics, hormonal changes, and health conditions, not washing or trimming.
3. Why is My Hair Falling Out as a Teenager?
Hormonal changes, stress, or underlying health conditions such as thyroid disorders or vitamin deficiencies can cause teenage hair loss.
4. What Is the Best Age To Get A Hair Transplant?
The best age for a hair transplant is usually when hair loss has stabilized. Many experts suggest waiting until around age 25-30 to ensure the loss pattern is clear.
5. What Nutrients Are Important for Healthy Hair During Pregnancy?
Iron, biotin, vitamin D, folic acid, and protein are essential nutrients for healthy hair during pregnancy. These nutrients support hair follicle health and overall hair growth, so it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet.
6. How Does Stress Affect Hair Loss During Pregnancy?
Stress can trigger telogen effluvium, a condition in which hair follicles prematurely enter the resting phase, leading to increased hair shedding. Managing stress with relaxation techniques like prenatal yoga and deep breathing can help reduce its impact on hair health.
7. Can I Use Hair Products During Pregnancy to Help With Hair Loss?
Yes, gentle, sulfate-free shampoos, conditioners with biotin, and other hair care products designed for pregnancy are safe and can help nourish the scalp and promote hair health. Avoid harsh chemicals and heat styling that could further damage hair.
8. Can Hair Loss Be a Sign of a Serious Health Condition During Pregnancy?
In most cases, hair loss during pregnancy is temporary and related to hormonal changes temporary and. However, if the shedding is severe or accompanied by other symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to rule out underlying health conditions like thyroid disorders or iron deficiency.
9. What Can I Do If My Hair Loss Continues After Pregnancy?
If hair loss persists beyond the postpartum period, it may be due to other factors like stress or nutrient deficiencies. Consult a doctor or dermatologist to evaluate your condition and explore treatment options such as hair growth medications or a hair transplant.
10. How Does Genetics Influence Hair Loss During Pregnancy?
Genetics plays a role in how hair loss manifests during pregnancy. If your family has a history of thinning hair or pattern baldness, you may be more likely to experience similar issues. Understanding your genetic predisposition can help you manage hair health more effectively.
Conclusion
Hair loss during pregnancy is a common concern, but it is typically temporary and can be managed properly. By focusing on a balanced diet, managing stress, and using gentle hair care products, women can help mitigate the effects of hair loss during pregnancy. Remember, this phase is usually short-lived; with time, your hair will return to its natural growth cycle. If the shedding persists or becomes more severe, consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can help you explore further treatment options. For a more personalized and effective treatment plan, Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County offers advanced solutions tailored to your needs, helping you regain confidence in your hair’s health and appearance.













Recent Comments