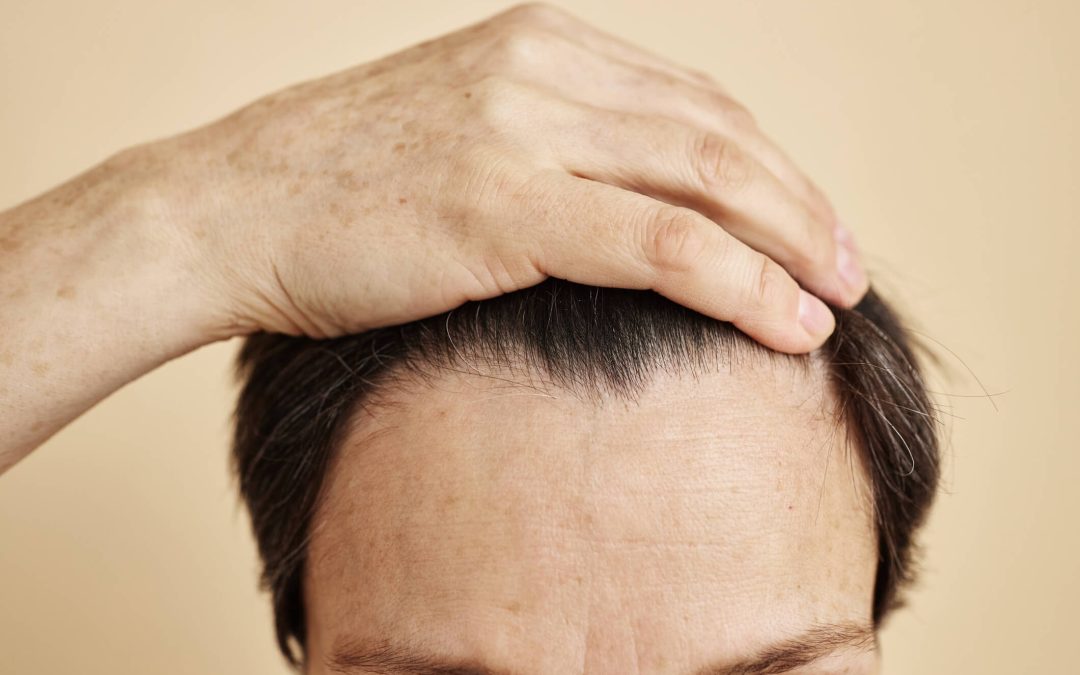
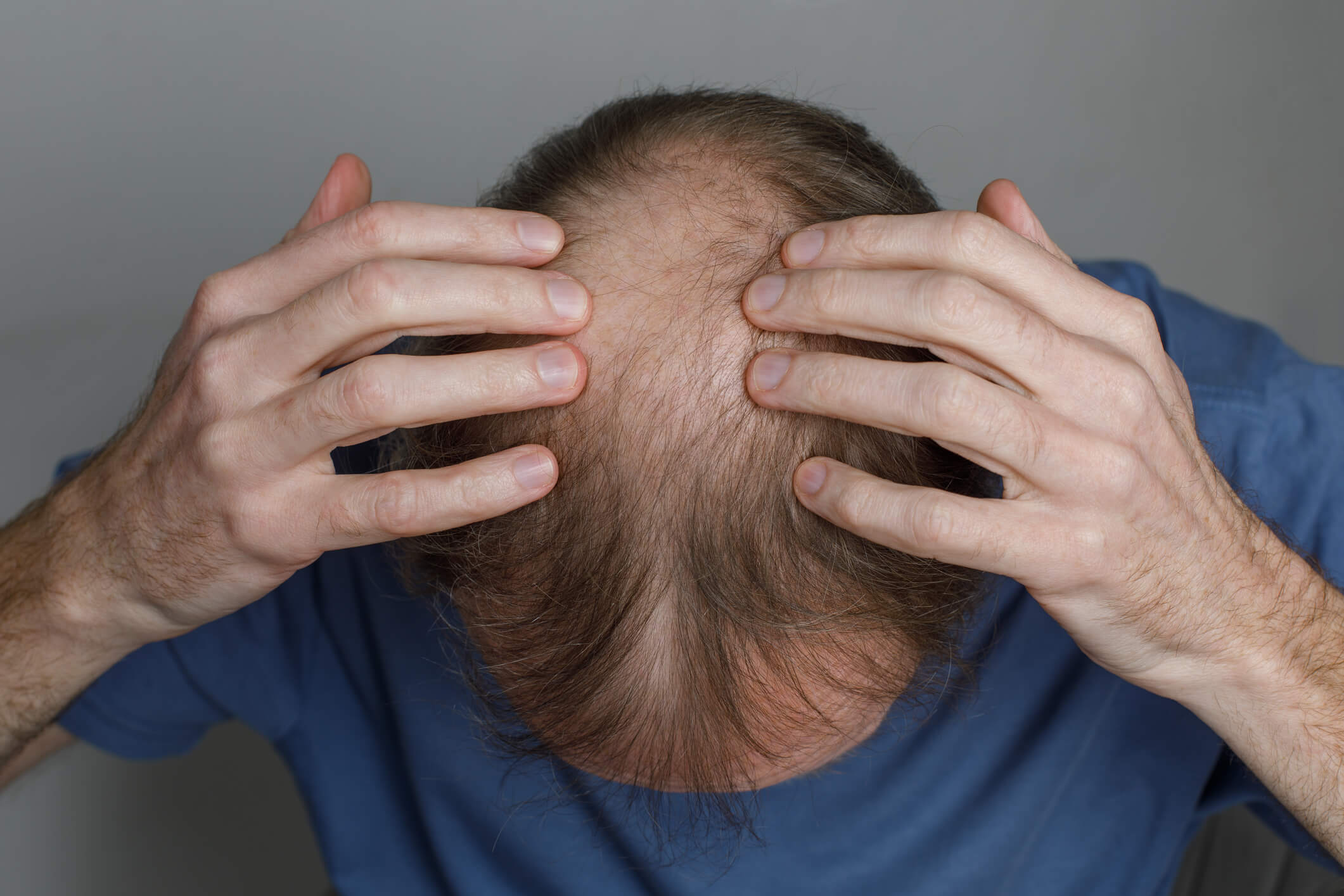
One of the most prevalent changes that females and males observe as they age is a change in their hairline. However, how can one differentiate between a receding and a mature hairline? It is crucial to comprehend the distinction between the two, as it is crucial to ascertain whether you are experiencing a typical aging sign or the initial phase of hair loss, even though both involve a hairline movement. In this blog post, you will learn about mature hairline vs receding hairline. Let us examine the primary attributes and disclose the pertinent information regarding each.
Definitions and Characteristics
One of the most prevalent changes that males observe as they age is a change in their hairline. However, how can one differentiate between a receding and a mature hairline? It is crucial to comprehend the distinction between the two, as it is crucial to ascertain whether you are experiencing a typical aging sign or the initial phases of hair loss, even though both involve a hairline movement. Let us examine the primary attributes and disclose the pertinent information regarding each.
What is the definition of a mature hairline?
A matured hair is an ordinary progression that begins in the mid to late 20s and continues as you age. Your hairline was likely straight and low on your forehead as an adolescent. This hairline typically elevates slightly as one age, resulting in a subtle “M” shape. This procedure is entirely standard and should not be confused with hair loss.
The primary characteristics of a mature hairline are as follows:
- Minimal Hair Loss: The hair on the scalp is generally thick and full, with a minor recession at the temples, indicating a mature hairline.
- Hairline Stability: The hairline typically remains in this position without further recession once it has matured.
- Age Factor: This transformation is common in men in their late 20s to early 30s.
What is a hairline that recedes?
Conversely, a hairline that recedes is characterized by a gradual loss of hair that results in a deepened “M” shape and thinning at the temples. In contrast to mature hair, a declining hairline is characterized by a progressive retraction, frequently resulting in baldness.
The primary indicators of a hairline that recedes are as follows:
- Continuous Hair Loss: A hairline that recedes, in contrast to a mature hairline, is characterized by continuous hair thinning, particularly in the temple area.
- Irregular Hairline: The hairline may appear irregular due to the recession being more apparent on one side.
- Early Onset: A hairline that recedes can begin in the early teens or 20s and progress faster than a mature hairline.
- Genetic Variables: A hairline that recedes is typically one of the first indications of male-pattern balding, which is frequently hereditary.
Methods for Differentiating Between the Two
The rate of hair loss and the location of the recession are the distinguishing factors between a mature hairline and a hairline that recedes. You are likely experiencing a mature hairline if your hairline has moved slightly but has since stabilized, and the remainder of your hair remains thick. However, if the hair continues to thin and recede, particularly in the area of the temples and crest, it may indicate a hairline that recedes.
Is there cause for concern?
A mature hairline is a natural consequence of maturing and does not necessitate any treatment. Nevertheless, it may be beneficial to seek the advice of a dermatologist or hair specialist if you believe you are experiencing a receding of hair. The progression of hair loss can be slowed by early intervention, which includes treatments such as:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a topical treatment that inhibits hair loss and stimulates growth.
- Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral medication that inhibits the hormone responsible for baldness.
- Hair Transplants: In severe hair loss, a hair transplant can restore hair in depleted areas.
Causes of Mature Hairlines
A mature hairline is a natural and gradual shift in the position of the hairline that occurs in males as they age. This process is regarded as a regular aspect of aging and is distinct from male or female-patterned baldness. A variety of factors influence the development of a mature hairline:
The Process of Natural Aging
Hormonal fluctuations induce modifications in hair growth patterns in men as they age. The hairline is typically low and linear across the forehead during adolescence and early adulthood. It is not uncommon for the hairline to recede slightly, particularly at the temples, resulting in a subtle “M” shape by the mid to late 20s. This change indicates the natural aging process and typically does not persist after the hairline has matured.
Genetic Variables
The development of a mature hairline is significantly influenced by genetics. If the males in your family experienced a similar change in their hairline at a certain age, you will probably, too. This hereditary factor is not linked to baldness; it is associated with a typical hairline maturation that varies from individual to individual.
Alterations in Hormones
Fluctuations in hormones, particularly androgens (such as testosterone and its derivative dihydrotestosterone or DHT), can influence hair growth as males age. This can cause the hairline to shift back during early adulthood, resulting in the usual mature hairline pattern. However, this sensitivity to hormones is significantly less severe than that observed in baldness, highlighting the distinction between the two.
Stabilization of the Hairline
The body’s adaptation to age-related changes typically results in developing a mature hairline, stabilizing once it advances upward. This stabilization suggests that the hairline has matured and is unlikely to continue to recede. Devoid of progressive deterioration, a mature hairline differs from receding hair.
Hair Growth Cycle That Is Non-Pathological
It is crucial to recognize that the overall hair development cycle, which encompasses hair growth, rest, and shedding phases, remains unaltered and healthy as the hairline matures. The minor movement of the hairline is a result of the body’s adaptation to the aging process rather than a sign of significant hair loss or deterioration of hair follicles.
Age Factors and Hairline Changes
Hairline changes are prevalent among men as they age and can differ significantly from individual to individual. It is essential to comprehend the typical patterns of hairline development and how age influences these changes to differentiate between normal aging and more alarming hair loss symptoms. The hairline is influenced by age in the following ways:
Late Adolescence: Teenage Years to Early 20s
Men typically have an adolescent hairline during adolescence and early adulthood. This hairline is low on the forehead and often has a straight, even appearance. It is prevalent during her teenage years and may persist into her early 20s.
- Hairline Characteristics: A linear, low hairline that extends across the forehead.
- Key Point: As men progress into their mid-20s, they will ultimately transition from this juvenile hairline to a more mature hairline.
Mid to Late 20s (Hairline Maturation)
For most men, the hairline typically matures in the mid-to-late 20s. This process involves a slight recession at the temples, which produces an “M” shape rather than the straight line observed in earlier years. This transition is a typical aging process and does not indicate baldness.
- Hairline Features: The hairline slightly recedes, particularly at the temples, but remains relatively complete and stable.
- Key Point: This transition is known as a mature hairline and typically returns to its original state after this period.
30s to 40s (Stabilization or Recession)
Most men develop a mature hairline by the time they reach their thirties. This hairline remains consistent for individuals who do not have a genetic predisposition to hair loss. For men experiencing baldness, the hairline may continue to recede into their 30s and 40s.
- Hairline Characteristics: Stable Mature Hairline: The hairline remains mature with minimal further recession for males who do not exhibit balding tendencies.
- Hairline Receding: Men genetically predisposed to hair loss experience a hairline that recurs, frequently producing a more pronounced “M” shape and thinning at the temples.
- Primary Point: A stable hairline in the 30s and 40s suggests that the individual will likely undergo an average, non-pathological hairline change.
Late 40s to 50s (Possible Thinning)
Even if their hairline has remained stable throughout their 30s, some men may begin to experience hair thinning by the time they reach their late 40s or early 50s. This thinning may affect the entire scalp, although it may be more apparent at the temples or crest. The hair growth cycle, hormonal alterations, and the cumulative effects of aging all contribute to the natural decrease in hair density as we age.
Hairline Characteristics:
- Hair loss at the temples and crown: Hair may diminish but does not necessarily recede significantly at the hairline.
- Progression of the Recession: Hair loss may persist during this phase for individuals genetically predisposed to baldness.
- Key Point: Hair thinning at this age is frequently a natural occurrence with aging; however, it may be managed through medical interventions if desired.
Hair Loss and Balding in the 60s and Beyond
The hairline and overall hair volume typically endure further changes in the 60s and beyond, with many men experiencing some hair loss. At this juncture in life, even men who do not have a family history of baldness may observe a decrease in hair density or an increase in hairline.
Hairline Characteristics:
- Increased Thinning or Recession: Hair loss may be more prevalent, although not all men will experience significant baldness.
- Advanced Pattern of Baldness: Men with baldness may experience severe thinning or complete hair loss at the crest as their hairline recedes further.
- Key Point: Hair loss and a higher hairline in the 60s are typically associated with the natural aging process; however, medication or hair restoration treatments may still be effective.
Genetic Influences on Hairlines
Genetics significantly influences baldness, determining whether a man will develop a mature hairline. Hereditary factors, frequently transmitted from both sides of the family, significantly influence the evolution of hairlines over time. A more comprehensive examination of the genetic factors that influence hairlines is presented below:
Hairline Patterns and Family History
The hairline history of close relatives, particularly parents and grandparents, can frequently be used to predict hairline development, whether it results in a stable, mature, or balding. Men who inherited baldness from their fathers, brothers, or grandfathers are likelier to experience comparable hair loss patterns.
- Inherited Traits: The genes that regulate hair development and hairline patterns are inherited from both parents. Early onset hairline recession is more likely to occur in individuals with a significant family history of baldness.
- Mother’s Side Influence: It is widely believed that baldness is inherited from the mother’s side of the family due to the X chromosome, which contains the androgen receptor (AR) gene. This gene significantly influences the sensitivity to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can induce hair loss. Nevertheless, hair loss is a multifactorial trait that is also influenced by heredity from the father’s side.
The Impact of Androgens and DHT Sensitivity
The sensitivity of your hair follicles to androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone, is influenced by the androgen receptor (AR) gene. The hair follicles of men with a genetic predisposition to hair loss are more susceptible to DHT.
- Hair Loss and DHT: Due to their high sensitivity to DHT, hair follicles undergo miniaturization, resulting in gradual shrinkage. Eventually, this leads to follicle mortality and thinner hair, contributing to baldness.
- Androgenetic alopecia, or baldness, is primarily caused by a genetic predisposition to DHT sensitivity. This condition results in a progressively balding and thinning at the crown.
Mature Hairline vs. Receding Hairline
Genetics determines the development of a mature hairline, which stabilizes after a minor recession, where hair loss continues progressively due to baldness.
- A slight upward shift in the hairline during the late 20s is frequently a genetic trait indicating the transition to a stable, mature male hairline. If your male relatives exhibit comparable hairline patterns, you will probably emulate them. This form of hairline does not cause baldness.
- Hairline Recession: In men genetically predisposed to male-pattern baldness, the hairline continues to recede beyond the typical aging. This genetic trait is associated with the progressive nature of hair loss, which frequently results in a more profound “M” shape or hairline reduction around the temples and crown.
Genetic Expression Variability
Genetics and the development of male-pattern baldness influence the age of onset and severity of hair loss. Due to genetic expression, some individuals experience early hairline recession in their late teens or early 20s, while others may experience significant changes in their 30s or later.
- Early Onset Hair Loss: Males who begin to lose hair in their 20s frequently exhibit a strong genetic predisposition to baldness, mainly if male relatives on both sides of the family experienced comparable patterns.
- Later Onset: Despite a genetic predisposition, certain males may experience hairline changes in their 40s or 50s. The influence of numerous alleles can significantly vary the rate and extent of hairline recession.
Genetic Testing for Hair Loss Prediction
In light of recent developments in genetic research, it is now feasible to administer a genetic test to ascertain the probability of hair loss. These assays analyze the presence of specific genes, such as the androgen receptor gene, that influence DHT sensitivity. Although these tests can offer insight into your prospective risk of developing baldness, they are not definitive.
Predictive Value: Genetic testing can help determine whether one’s hairline will remain mature or recede, enabling early intervention with treatment if necessary.
Signs of Progression: Mature vs. Receding
Identifying whether the changes in your hairline are a natural part of aging or an early indicator of baldness requires understanding the progression of a mature hairline versus receding hair. Each exhibits a unique progression pattern that is readily apparent. The following is a comprehensive examination of the distinctions:
Mature Hairline Development
A mature hairline is characterized by a modest and all-natural upward shift in the hairline, which stabilizes and does not suggest ongoing hair loss. The signs and phases of a mature hairline are as follows:
- The initial transition in hairline occurs during the mid to late 20s.
- The hairline typically ascends approximately 1 to 1.5 cm from adolescence.
- The temples are the primary location of recession, resulting in a mild “M” shape.
- The remainder of the hairline is unaltered and complete.
Major Point: This transition is incremental and will reach a state of equilibrium as the hairline matures.
- Stabilization (Late 20s to Early 30s)
- The hairline ceases to recede after a slight upward movement and remains in its new, slightly elevated position.
- The remainder of the scalp appears to have dense, healthy hair, and no additional indications of hair thinning are present.
Key Point: The hairline stabilizes following this minor shift and does not continue to recede with age.
- Absence of Hair Loss or Thinning
- The hairline’s hair remains dense and robust, with no indications of further thinning or miniaturization of hair follicles.
- The density of hair in the remaining portion of the skull remains unaffected.
Major Point: The presence of a mature hairline is not accompanied by persistent hair thinning or loss at the temples, crest, or top of the head.
- Long-Term Stability
- Hair loss only progresses significantly in men with a mature hairline as they age into their 30s, 40s, and beyond.
Key Point: The development of a mature hairline is a single event that occurs early in life and remains consistent over time.
The Development of a Balding
The progression of baldness (androgenetic alopecia), characterized by continuous hair loss, includes balding. If left untreated, the progression is more pronounced and continuous, frequently resulting in baldness.
Early Signs of Recession (Late Teens to 20s)
The hairline frequently begins to form a more profound “M” shape than it does in a mature hairline, as recession frequently commences at the temples.
The hairline may become less defined, and hair may begin to recede at the temples.
Key Point: Hair loss typically commences earlier than a mature hairline and persists over time.
Continuous Hairline Recession (Late 20s to Early 30s)
The hairline recurses on the forehead, resulting in a more pronounced “M” or widow’s peak.
Particularly at the temples and in the direction of the crown, the thinning becomes more apparent.
Key Point: Unlike a mature hairline, the recession does not stabilize and persists over time.
Thinning hair at the crown (mid to late 30s)
Thinning at the crown or top of the skull is frequently apparent as the hairline recedes.
The hair in these regions becomes more sparse and finer, contributing to a general decrease in hair density.
Key Point: Hair receding is frequently accompanied by crown thinning, a defining characteristic of baldness.
Hairline Widening (The late 30s to 40s)
The forehead may appear more prominent as the hairline recedes further and may widen at the temples.
As the “M” shape intensifies, the temples may become completely bald, resulting in a horseshoe-shaped pattern of hair around the sides and back of the head.
Key Point: The hairline is receding, and hair depletion is accelerating, particularly in the crown and temples.
Baldness in the advanced stages (50s and beyond)
In the most advanced phases, the thinning of the crown may intersect, resulting in a bald scalp on the front and top of the head.
The hair is typically only left on the sides and rear of the head in a typical “U” or horseshoe pattern.
Key Point: This stage indicates advanced baldness, in which the majority of hair on the crown of the head is removed.
Psychological Impact of Hairline Changes
Changes in the hairline, whether due to natural aging or baldness, can have a substantial psychological influence on numerous individuals. Hair is frequently associated with an individual’s self-esteem, perceived attractiveness, and sense of identity. Men may encounter a variety of psychological and emotional consequences as their hairline changes. Here is a more detailed examination of the psychological consequences of hairline changes, which includes effective coping mechanisms.
Confidence and Self-Esteem
Hair loss, mainly when it occurs unexpectedly or prematurely, can result in feelings of insecurity or diminished self-esteem. In a society where a full head of hair is frequently associated with youth and vitality, a receding of hairline or perceptible thinning often challenges an individual’s self-perception.
- Mature Hairline: The gradual and stable shift may not be as emotionally distressing for individuals with a mature hairline who experience a minor recession. Nevertheless, certain males may still experience a decline in self-assurance, mainly if they interpret the alteration as an indication of their age.
- Receding Hairline: The ongoing nature of hair loss can produce a sense of losing control over one’s appearance, leading to more pronounced anxiety, particularly when it progresses rapidly. Men with thinning of hairline may experience feelings of self-consciousness, resulting in social withdrawal or a reluctance to participate in activities that attract attention to their appearance.
Perception and Body Image
How individuals perceive their hairline can significantly impact their overall body image. Hair is a conspicuous feature, and its loss or alteration can significantly influence an individual’s perception of their attractiveness. This can result in an individual’s perception of themselves being distorted, as they may perceive themselves as significantly aged or less attractive than others.
- Body Image Issues: Men experiencing a receding of hair may find their changing appearance inconsistent with their self-image. This discrepancy between self-perception and actuality can result in embarrassment, frustration, or shame.
- Comparisons with Peers: Men may experience feelings of inferiority when they observe their friends or associates maintaining a full head of hair, which can result in them comparing themselves unfavorably to others. The disparity in appearance may exacerbate insecurities, further reducing body image gratification.
Anxiety Related to Age
Hairline changes, particularly thinning hairlines, can be a visible reminder of aging and elicit anxiety. For many individuals, Balding is one of the first outward indications of aging, which can result in stress or even fear regarding the future.
- Premature Aging: Men who experience early hairline recession, sometimes as early as their 20s, may experience emotional distress due to the perception that they are aging prematurely. This perception may encompass apprehensions regarding romantic relationships, career prospects, or overall life satisfaction.
Professional and Social Consequences
In certain circumstances, modifications to one’s hairline can influence one’s emotional state in professional or social environments. The degree of comfort an individual experiences when engaging with others can be influenced by the pressure to adhere to specific attractiveness or grooming standards.
- Social Anxiety: Men experiencing a receding of hair may avoid specific social situations or feel apprehensive about how others will perceive them. This anxiety may be a result of concerns about being perceived as less attractive or older.
- Professional Environment: In professional environments, individuals with noticeable hair loss may fear being evaluated based on their appearance, which may lead colleagues or clients to associate hair loss with age-related issues or declining vitality, even if the individual’s performance remains uncompromised.
Emotional Distress and Depression
In more severe instances, hairline changes can result in more profound emotional issues, such as melancholy. Mental health challenges, particularly in men who struggle with acceptance of their altered appearance, have been associated with hair loss.
- Depression: A hairline that is receding can induce depressive symptoms in men who prioritize their appearance. This may encompass sentiments of despair, melancholy, or diminished enthusiasm for activities that they previously relished.
- Identity Crisis: Some men may experience a sense of loss of self-identity, mainly if their appearance has been a significant factor in their social or professional life, as hair is frequently associated with identity.
Coping Mechanisms
The management of hairline alterations necessitates both emotional and practical strategies. Although the psychological effects can be challenging to manage, several coping mechanisms can assist individuals in reducing the emotional distress that is associated with hair loss:
- Acceptance: The ability to embrace natural changes in appearance can reduce anxiety. This entails acknowledging that hair loss is a prevalent experience for many men and does not diminish their value or self-worth.
- Hair Restoration Treatments: For individuals dissatisfied with the modifications to their hairline, there are numerous medical alternatives, including hair transplants, topical treatments such as minoxidil, and oral medications like finasteride. These remedies can assist in slowing or reversing hair loss, granting a sense of control over the process.
- Style Changes: Adopting a new hairstyle, such as a wholly shaved head or a close-cropped look, can be empowering. Numerous men discover that incorporating a new style in harmony with their evolving hairline can enhance their self-assurance and alleviate feelings of insecurity.
- Emotional Support: Conversing with a therapist or participating in a support group can establish a secure environment for expressing emotions associated with hairline changes. Acknowledging that others experience comparable challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Perspective Shifts: Concentrating on other aspects of life, such as personal accomplishments, relationships, or health, can help one better understand hair loss. Many males discover that diverting attention from appearance-based concerns enhances their overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Receding Hairlines
It can be a distressing experience; however, various treatment options are available to slow down or reverse hair loss. These treatments encompass a variety of options, including medical therapies, lifestyle modifications, and cosmetic procedures. The appropriate treatment plan is contingent upon the stage of hair loss, underlying causes, and personal preferences. The following is a summary of the most prevalent and efficient alternatives:
Pharmaceuticals
Several FDA-approved medications are available to treat hair loss, with a particular emphasis on baldness. In some instances, these treatments are most effective in reducing hair loss and, in certain cases, regrowing hair in thinning areas.
Rogaine (Minoxidil)
- What It Is: Minoxidil is a topical treatment that enhances blood supply to hair follicles, prolonging the growth phase of the hair cycle and stimulating hair growth.
- Method of Use: Directly apply the scalp twice every day.
- Effectiveness: Minoxidil has been demonstrated to retard hair loss and, in certain instances, stimulate hair regrowth along the hairline and crest. Results typically manifest over several months.
- Potential adverse effects include scalp irritation, itching, and unwanted hair growth in areas other than the scalp.
Finasteride (Propecia)
- What It Is: Finasteride is an oral prescription medication that decreases dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, the hormone that causes hair follicles to diminish in a pattern of baldness.
- Instructions for Use: Daily administration in capsule form.
- Efficiency: Finasteride has been demonstrated to decrease hair loss and, in numerous instances, stimulate hair regrowth. It is notably effective in reducing the progression rate of balding.
- Side Effects: Certain users may experience side effects, including a decrease in libido, erectile dysfunction, and a depletion of semen volume. Although these adverse effects are uncommon, they may persist even after the medication is discontinued.
Dutasteride (Avodart)
- It is similar to finasteride but inhibits both forms of 5-alpha-reductase, the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. It is frequently prescribed off-label for hair loss.
- Effectiveness: Research indicates that dutasteride may be more effective than finasteride in promoting regrowth and slowing hair loss, even though it is associated with a comparable risk of adverse effects.
- Adverse Effects: Sexual adverse effects are possible, similar to those of finasteride.
Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery is a permanent solution for males experiencing significant hairline recession. This procedure entails relocating hair follicles from the back or sides of the scalp to areas where hair has receded or thinned.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is a procedure in which a strip of scalp is removed from the rear of the head, and individual hair follicles are extracted and transplanted to the receding hairline or other thinning areas.
- Advantages: It is more cost-effective than other surgical options and can cover larger areas in a single session.
- Cons: A linear scar is left at the donor site, which may be visible if the hair is cropped short.
What is Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)? In FUE, hair follicles are harvested directly from the scalp and transplanted to the thinning areas without removing a section of the scalp.
- Advantages: FUE is less invasive than FUT, resulting in a shorter recovery. Additionally, it does not produce a linear scar.
- Cons: It may be more costly and time-consuming, as only small areas can be treated during each session.
The efficacy of hair transplants
FUT and FUE are highly effective in restoring hair in areas of recession, particularly the hairline. The results are permanent, although it may take several months for the full extent of the results to be apparent as the transplanted hair follicles grow naturally.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LT)
- What It Is: LLLT is a non-invasive hair growth treatment that employs red light lasers to stimulate hair follicles. It can be performed at home using laser caps, combs, or headwear.
- Effectiveness: Research indicates that LLLT can help prevent hair loss and, in certain instances, promote hair growth. It is most effective when combined with other treatments, such as finasteride or minoxidil.
- Advantages: Minimal side effects, non-invasive, and benign.
- Cons: It may only suit some individuals and necessitates long-term use to maintain results.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Definition: PRP therapy entails extracting a small quantity of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the plasma into areas of diminishing or receding hair. Platelets contain growth factors that aid in stimulating hair follicles and promoting hair regrowth.
- Effectiveness: PRP has demonstrated promising results in promoting hair density and reducing hair loss, mainly when used with other treatments.
- PROS: Utilizes the body’s natural healing mechanisms to promote hair growth and is non-surgical.
- Cons: It may necessitate multiple sessions, may be costly, and outcomes may differ among individuals.
Wigs and Hairpieces
For individuals interested in a nonmedical alternative, hairpieces and wigs can offer immediate coverage for balding. Modern hairpieces are designed to resemble natural hair and can be customized to match the individual’s hair type and color.
- Advantages: Provides a temporary solution without the necessity for surgery or medication, immediate results, and is non-invasive.
- Cons: Maintenance is necessary, and some individuals may experience feelings of self-consciousness when wearing a hairpiece.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle
Although not as effective as medical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications and natural remedies can slow the progression of hair receding and promote healthy hair.
- Healthy Diet: A diet that is abundant in vitamins and minerals, particularly those that promote hair health, such as biotin, zinc, iron, and vitamins A, C, and E, can assist in the preservation of healthy hair. Hair resilience and growth can be enhanced by consuming foods such as nuts, leafy greens, and lean proteins.
- Managing tension through meditation, yoga, or exercise techniques may help slow hair loss, as stress can contribute to hair loss.
- Scalp Massage: The scalp can stimulate blood flow to hair follicles, promoting hair growth. Although it is not a viable solution for substantial hair loss, it can be an adjunct to other treatments.
Combination Therapy
In numerous instances, using multiple remedies can produce superior outcomes when contrasted with a single approach. For instance,
- The combination of finasteride and minoxidil is frequently employed to address baldness.
- PRP therapy can be implemented in conjunction with hair transplants to expedite the healing and regrowth process.
- LLLT has the potential to enhance the effects of medications such as minoxidil.
Styling Tips for Different Hairline Types
The appropriate hairstyle can improve your appearance and increase your self-assurance, regardless of maturity. The following are a few suggestions to assist you in styling your hair according to the type of hairline you have:
Hairstyle Advice for Mature Hairlines
A mature hairline is subtle and stable, which makes it effortless to manage with a diverse array of hairstyles.
- Classic shortcuts, such as crew cuts or buzz cuts, are low-maintenance and can help detract attention from the hairline. They establish a harmonious appearance that emphasizes facial features.
- Textured or Layered Styles: By incorporating layers or a messy, tousled appearance into the top of the hair, you can create volume and reduce the visibility of the hairline. Employing a matte styling product achieves a natural, luxuriant look.
- Classic side part: A mature hairline is ideal for a side part. It can enhance the appearance of fullness and provide structure to the hair. For a refined appearance, maintain a longer top and shortened sides.
- Medium-length hairstyles can reduce the appearance of a mature hairline. Allowing the hair to grow slightly increases the ability to experiment with various designs.
Hairstyle Suggestions for Receding Hairlines
Balding necessitates more strategic grooming to maintain confidence and conceal thinning areas.
- Buzz Cut: A buzz cut is a highly sought-after option for men with thinning hairlines. It reduces the contrast between the thinning areas and the remainder of the hair, obscuring the hairline.
- Shaved Head: Adopting a wholly shaved head is bold and fashionable for men with a substantial hairline recession. It eliminates the emphasis on slender areas and provides a sleek, clean appearance.
- High Fade or Crew Cut: A high fade or crew cut maintains a slightly longer top while cutting the sides and back of the hair short. This style redirects attention upward and away from the thinning.
- Textured Crop: A texture with a fringe can conceal a receding of hair. In addition to concealing thinning along the hairline, the fringe and added texture at the front add volume.
- Comb-over (with caution): A contemporary comb-over involving combing hair to one side can be effective if executed discreetly. Avoid over-combing, as it can result in an unnatural appearance; maintain a light and natural appearance with a slight volume on top.
Tools and Products for Styling
- Products that increase volume: If you have sparse hair, it is recommended that you use a lightweight, volumizing mousse or powder to add fullness to your hair. It creates the impression of increased volume and density.
- Matte Pomades or Wax: Styling products with a matte finish can impart texture to the hair without causing it to appear greasy or sparse. These products are perfect for achieving natural-looking designs suitable for mature and receding airlines.
- Blow Dryer: A blow-dryer can help develop volume and lift at the roots. This is especially beneficial for men with receding hair, as it enhances the appearance of fullness and adds height.
Beard and Facial Hair
- Balanced Appearance: By growing a beard or maintaining facial hair, you can help balance a receding or mature hairline by directing attention away from the hairline and toward your facial features.
- Full Beard or Goatee: A full beard or goatee can create a sense of symmetry on your face and redirect attention from the hairline to the mandible.
Conclusion
It is essential to comprehend the distinction between mature and balding, particularly in females, to determine whether your frontal hair changes result from natural aging or the onset of male-pattern baldness. If you are uncertain, monitoring the hair loss rate and seeking a professional’s guidance for diagnosis and prevention strategies may be beneficial to ascertain the most effective course of action.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the distinction between a mature and receding hairline?
A mature hairline is a natural transition in the hairline that occurs as males age, typically receding by approximately 1–2 centimeters from the juvenile hairline. In the mid-to-late 20s, this process typically reaches a state of equilibrium. Conversely, balding is an early indicator of baldness, in which the hairline gradually recedes and may take on an “M” or “V” shape as the hair thins along the temples.
What is the age at which a mature hairline develops?
Men typically develop a mature hairline between the ages of 17 and 30. It is a typical aging process and frequently resolves without causing substantial hair loss. The process is subject to individual variation but typically concludes after a few years.
How can I determine whether I have a receding or mature hairline?
You probably have a mature hairline if the transition is gradual and subtle. This may occur in your late teens or early 20s. A specific point is typically the point at which it stabilizes. However, it is characterized by more aggressive hair loss, particularly in the temple area, and it may result in bald regions as it continues to thin over time.
Is it possible to address balding?
Various remedies are available, such as hair transplant surgery, low-level laser therapy (LLLT), medications such as finasteride and minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments. Early intervention typically slowed or reversed hair loss more effectively.
Is a mature hairline a sign of baldness?
No, a mature hairline is not inherently indicative of baldness. It is a typical, age-related adjustment that typically stabilizes. Baldness, or balding, is characterized by a consistent thinning or loss of hair that extends beyond a stable, mature hairline, frequently resulting in noticeable bald regions.
Mature Hairline vs. Receding Hairline: What You Need to Know with Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County!
Are you perplexed by the distinction between a mature hairline and receding hair? At Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County, we acknowledge that comprehending the changes in your hairline can be a profoundly personal and occasionally overwhelming experience. Our expert team of hair restoration specialists and surgeons is committed to offering you the necessary clarity and insights, and they are located in the lively community of Orange County, California.
For additional hair loss and restoration details, please refer to our previous blog posts: “Does Working Out Cause HairLoss?” and “Does Wearing a Hat Cause HairLoss?“
Do not hesitate to reclaim your appearance and increase your self-esteem! Contact us immediately to schedule your consultation and take the first step towards a healthier, fuller head of hair. The power to restore your hair and confidence is in your hands.













Recent Comments